If you’re planning to build a career in cybersecurity, your laptop is one of the most important tools you’ll invest in. Whether you’re running Kali Linux, setting up virtual machines (VMs), learning ethical hacking, or completing CTFs on TryHackMe or HackTheBox, you’ll need a powerful and secure system to keep up with your tasks.
In this blog, we’ve compiled the top laptops for cybersecurity training in 2025, based on performance, Linux compatibility, virtualization support, and overall value for money. These laptops are available on Amazon and are perfect for both beginners and professionals.
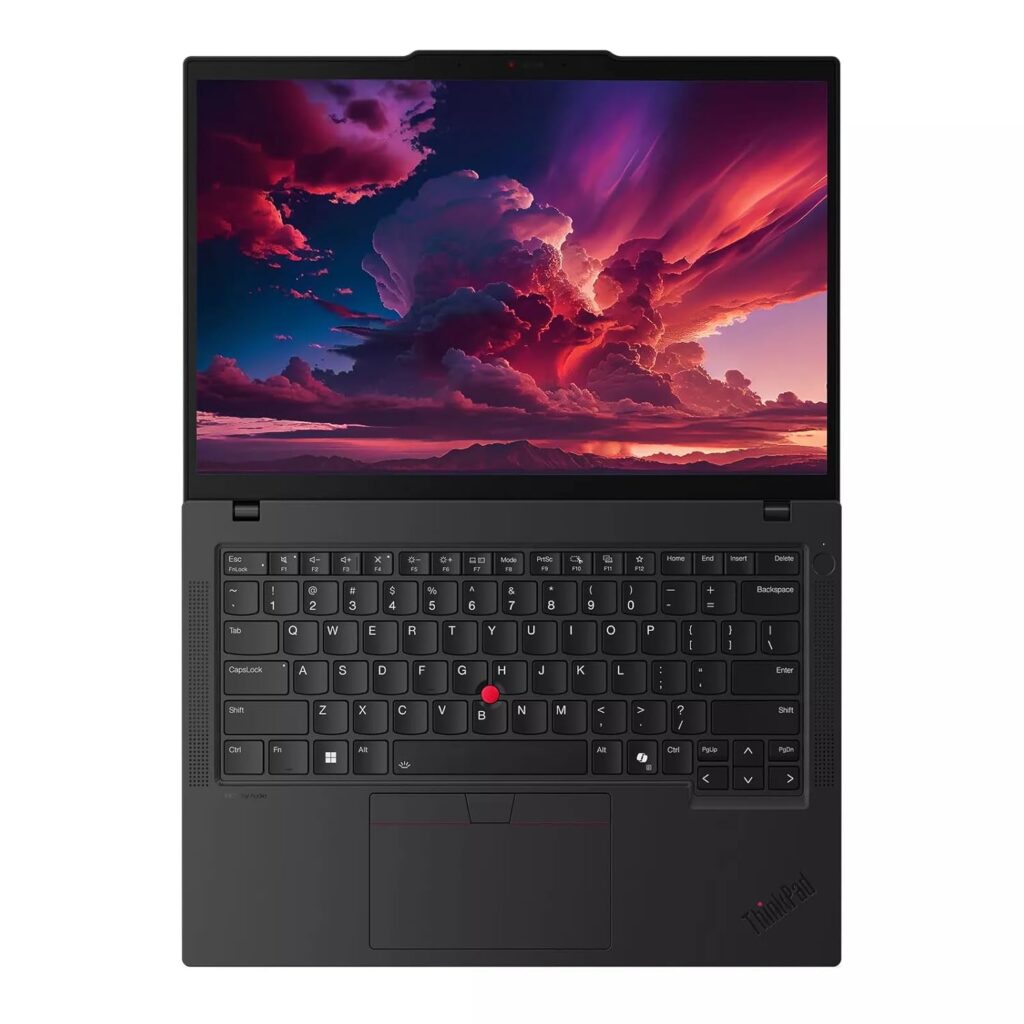
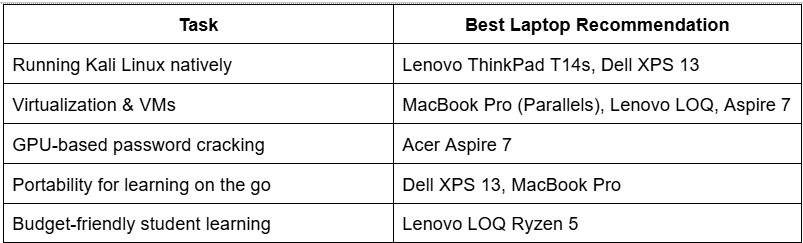
1. Lenovo ThinkPad T14s Gen 5 – Best Overall for Professionals
Processor: Intel Core Ultra 7
RAM: 32 GB
Storage: 512 GB SSD
Security: TPM 2.0, fingerprint sensor, privacy shutter
Why it’s great: ThinkPads are built for enterprise-level security and performance. They handle VMs, penetration testing tools, and Kali Linux without breaking a sweat.
🔗 [Buy Lenovo ThinkPad T14s Gen 5 – https://amzn.to/46J0ALN]
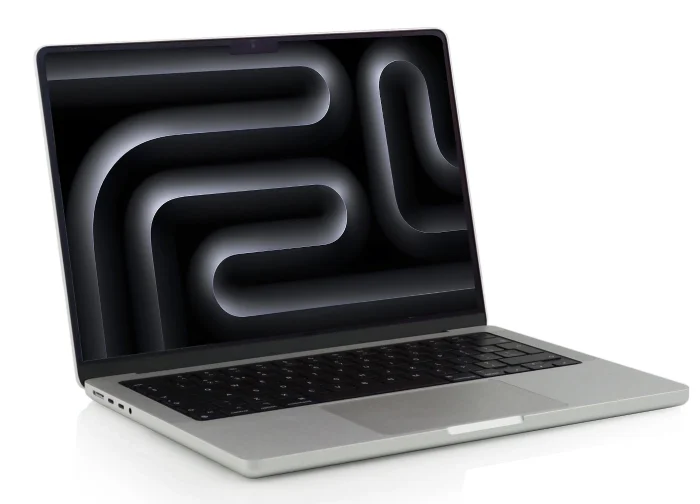
2. Apple MacBook Pro 14″ (M4) – Best for macOS + Cybersecurity Labs
Processor: Apple M4
RAM: 16 GB (upgradeable)
Storage: 512 GB SSD
Security: T2 chip, Secure Enclave, FileVault encryption
Why it’s great: Perfect for professionals who want macOS’s secure ecosystem while also running virtual machines using VMware or Parallels.
🔗 [Buy MacBook Pro 14″ (M4) – https://amzn.to/3UrX3Kd]
3. Dell XPS 13 Ultra – Best Linux-Friendly Premium Laptop
Processor: Intel Ultra 7
RAM: 32 GB
Storage: 1 TB SSD
Display: 13.4″ FHD+ InfinityEdge
Why it’s great: Lightweight, premium, and highly compatible with Linux distros like Kali and Ubuntu. Ideal for on-the-go ethical hackers.
🔗 [Buy Dell XPS 13 Ultra – https://amzn.to/40BhXu1]
4. Samsung Galaxy Book4 – Best Display + Secure Hardware
Processor: Intel Ultra 7
RAM: 16–64 GB
Storage: 512 GB SSD
Display: Super AMOLED
Security: Samsung Knox Vault
Why it’s great: Beautiful display, great battery life, and strong built-in security. A great Windows-based alternative for cybersecurity learners.
🔗 [Buy Samsung Galaxy Book4 – https://amzn.to/3TVHLgE]
5. Acer Aspire 7 Gaming Laptop – Best for GPU-Powered Tools
Processor: AMD Ryzen 5 / Intel i5 options
RAM: 16 GB
Storage: 512 GB SSD
Graphics: NVIDIA GTX or RTX
Why it’s great: For those learning password cracking, GPU-accelerated tasks like Hashcat, or 3D visualizations—this gaming laptop gives both performance and affordability.
🔗 [Buy Acer Aspire 7 – https://amzn.to/454G1GO ]
6. Lenovo LOQ Ryzen 5 – Best Budget Laptop for Students
Processor: AMD Ryzen 5
RAM: 16 GB
Storage: 512 GB SSD
Why it’s great: A solid choice for students or beginners who want to start learning Kali Linux and basic networking without breaking the bank.
🔗 [Buy Lenovo LOQ Ryzen 5 – https://amzn.to/3UwcGjK]
Ideal Use Cases Across the List:
What to Look for in a Cybersecurity Laptop
Before buying a laptop for cybersecurity, make sure it includes:
- Powerful CPU – At least Intel i5 or AMD Ryzen 5
- 16 GB RAM or more – For smooth multitasking and VMs
- 512 GB SSD – Faster boot, tool installs, and response
- Virtualization Support – Enable VT-x or AMD-V in BIOS
- Linux Compatibility – Works well with Kali Linux or Ubuntu
- Secure Hardware – TPM 2.0, fingerprint reader, encryption tools
Choose the Right Laptop for Your Cyber Lab
Choosing the right laptop for cybersecurity training is not just about speed or price—it’s about reliability, performance, and compatibility with the tools and technologies you’ll use every day. Whether you’re diving into ethical hacking, penetration testing, or network defense, your machine must support everything from Kali Linux and virtual machines to packet sniffing and secure browsing.
From the professional-grade Lenovo ThinkPad T14s to the sleek and powerful MacBook Pro M4, and the budget-friendly Lenovo LOQ Ryzen 5, this curated list gives you a laptop for every level and purpose.
🔗 Ready to build your cyber lab?
Check out our blog here
Tip for Students & Beginners:
If you’re just starting out, invest smartly. Begin with a reliable mid-range machine like the Acer Aspire 7 or Samsung Galaxy Book4, and upgrade as your needs evolve.
Tip for Professionals & OSCP Aspirants:
Choose a laptop with 32 GB RAM, a high-end CPU, and Linux compatibility for handling multiple VMs, CTF platforms, and advanced toolkits.
Your cybersecurity career deserves a powerful launchpad—invest in a laptop that works as hard as you do.
Team CyberiumX